(A), hazelnut weevil ã€Hazardous】
Hazelnut weevil, also known as hazelnut, hazel. Adults feed on tender shoots, young leaves, and tender shoots. The tender shoots are incomplete, and the young leaves are pinhole-shaped, and the shoots are broken, which affects the growth of new shoots. Adults can also pierce the young fruit with an elongated head tube and feed the young embryos in the young fruit to form a brown-brown dry shrinkage in the fruit. The young embryos stop developing and the fruit fall off early. When the larvae plunge into the fruit, part or all of the hazelnuts are eaten and the feces are placed in the fruit.
This pest has more occurrences of wild flat hazelnuts in the northeastern region. The cultivated hazelnut has not yet found such pests, but it is necessary to increase vigilance and prevent the insects from passing through the cultivation garden.
ã€Life History and Habits】
The worm had two generations in Liaoning in two years and a few in three years and one generation. In 2 years and 1 generation, it usually takes the mature larvae and adults to live in the soil for 3 years. It was unearthed in early May of the following year and began to operate under the litter layer. In mid-May, the adults went to the tree and began to eat young leaves. In late May, the adult enters its prime period. In the middle and late June, the hazelnut young fruit development period, when the adult began to copulate, lay eggs in young fruit. In the middle of July, the spawning period is high and the egg period is 10 to 14 days. In July Shangdian hatched larvae in fruit, and in mid-late July, it was the hatching period. Larvae feed on fruit for nearly 1 month and develop into mature larvae. In early August, when the hazelnuts mature, the mature larvae fall down to the ground. After the fruit is dehydrated, it is drilled into the soil and is ready for the winter at a depth of 20 to 30 cm. The middle and late August is a period of high earth. The beginning of the first year of July in the third year began.
In late July, it will enter the flood season and the flood season will be around half a month. New adult worms began to appear in mid-July, and the adult eclosion peaked in mid-August. The newly emerged adults will not be unearthed that year and they will be transferred to wintering conditions.
[control methods]
Hazel weevils have a wide range of occurrences, long and complex life history, overlapping generations alternately. Therefore, simply using chemical agents to prevent and control can not get ideal results, we must take a comprehensive approach to prevention and control.
(1) Chemical control In the supplementary nutrition period and the initial stage of spawning before adult oviposition, from mid-May to early July, 60% of DM mixture is used to kill adults with high concentration of 300 times and the hazelnuts are fully prepared. Treatment, even spray 2 to 3 times, ask the time interval is 15 days. The application amount is 0.1 kg per 667 square meters. Or use 50% nitrile loose emulsion and 50% chlordane emulsion, mix the two in a ratio of 1:4, and then spray them with 400 times solution to kill the adults. Before the larvae were de-fruited and the fruit was shed, that is, from late July to mid-August, 4% D-M powder was used to kill and remove fruit larvae on the ground. The dosage per hectare was 22.5 to 30 kg.
(2) When artificially controlling harvested hazelnuts, the fruit removal larvae are concentrated. That is, before the larvae have not been de-fruited, the insects are picked and then piled up on a clean concrete floor or a wooden board, and the larvae are collectively eliminated when the fruit is removed. For hazelnuts with particularly severe worm fruit, low yield, and no edible value, harvesting can be carried out in advance from late July to early August, and the pests can be collectively eliminated.
(b) The beetles are harmful to the beetles of the hazel tree. They are mainly black cashew beetle, apple hair beetle and betel green beetle.
1 Black cashmere chafer
[Harm] Harmful to the buds and young leaves of hazel trees.
ã€Life History and Habits】 One generation occurs in one year and the adults spend winter in the soil. In mid-April, the adult was unearthed. The peak of exhumation occurred from late April to early May. The adults climbed out of the earth before and after the sunset.
Fly to the tree to harm the buds, leaves, 21 to 22, but also hidden in the earth. Adults mostly ask for spawning eggs in wasteland, green manure or fields. Adults have a false death habit.
ã€Prevention and Control Methods】 In the adult harmful period, it can be poisoned under the canopy of the hazel tree. When the adults are harmed by trees, they are shaken off from the trees by hand, and the adults drill into the soil, and the poisoning is dead.
2 apple hair chafers
[Hazardous] The worm damages the young leaves of the hazel tree, and its larvae damage the young roots underground. When it happens, the adults colonize the leaves and eat all the young leaves.
ã€Life History and Habits】 One generation occurs in one year, and adults spend their winter in the soil. In mid-April, adults emerged to harm the leaves. Adults began to spawn in early May. The eggs are hatched after about 10 days.
Larvae feed on young roots. Until late autumn, the larvae emerged as adults and wintered in the soil. Adults do not move sooner or later. When the temperature rises before and after noon, adults fly into hazel trees to feed on the leaves. With a false death habits, a slight alarm that is landing.
ã€Prevention and control methods】 Use adult dead-dead habits. When adults do not move sooner or later, artificially shake off adult insects, stamp them to death, or sprinkle poison on the ground in advance. The effect is better. When the adult occurs, it can be sprayed and poisoned, and the effect is also very good.
3 bronze green chafer
[Hazardous] The worm damages the leaves of the hazel tree, incompletely bites the leaves, or eats all the light, leaving only the petiole.
ã€Life History and Habits】 One generation a year. The old mature larvae live in the soil. In May of the following year, he asked about phlegm. In the middle and late June, the adults emerged in feathers and began to harm. Adults are mostly active at night. From 19 to 20 o'clock in the evening, a large number of insects gather on the trees to harm the leaves. Adults have a strong phototaxis and suspended dead habits. Adults often produce eggs on planted legumes and pods. The eggs last for about 10 days. The hatched larvae endanger the roots.
ã€Prevention and Control Methods】 In the first half of June, the adult was sprayed and poisoned during the endangered period. When adulthood occurs, the phototaxis of the adult can be used to seduce with light, or ignite around the hazel orchard, so that the adult flies to the fire and is burned or shaken.
News entry: Mountain Benxi County, Liaoning Province Fruit farming cooperatives Update Time: 2012-3-22 14:12:35
How to trim the hazelnut tree: Leave a trunk and later prune it according to its own growth and development characteristics to form a reasonable skeleton. There are 3 types of trees commonly used, such as a little dry cluster shape, a single stem shape, and a multi-dry trunk shape. Less dry plexiform shape; leave 3-4 basal branches as main branches and obliquely extending in different directions. The main branch is borne with lateral branches, lateral branches with vegetative branches and resultant mother branches. The overall formation is still happy tree shape, single stem shape; this kind of tree shape to retain a trunk, choose to stay in the main trunk 3-4 uniform distribution of the main branch, the main branch on the election to stay on the side branch, the side branch on the birth of the vice branch and the resulting mother Branches, forming a dwarf trunk.
Multi-dried plexiform; this crown is selected 3-4 basal branches as the main branch, and the rest of the basal branches cut off from the base. If the basal shoots are less than the main branch number, they can be selected in the sprouting branches. After the main branch is selected, the resulting shoots and vegetative shoots are cultured.
Fifth, how to fertilize farmyard manure in early May, and catch compound fertilizer in mid-July. In the second year of planting, you can apply fertilizer outside the perimeter of the tree canopy. Don't chase it too deep.
IT02S, is JRT new product in the early 2019, which is a single-point LiDAR sensor, also called tof distance sensor. With a micro size of 46x17x7mm, customers can widely use in many Laser Measurement Solutions. The lidar distance sensor can measure 12m short-range with high frequency up to 100hz. It's great for Unmanned Aerial Systems. If you need us send you data sheet and spec for this products, offering sample as well, pls tell us, thank you.
Accuracy
+/-8cm@ 0.1~3.5m
Measuring Unit
cm
Measuring Range (without Reflection)
0.1-12m
Measuring Time
0.1~3 seconds
Measuring Frequency
100 Hz
Laser Class
Class II
Laser Type
650nm, <1mw, red
Weight
About 5g
Voltage
DC2.5V~+3.5V
Serial Level
TTL 3.3V
Size
46*17*7mm
Operating Temperature
0-40 ℃ (32-104 ℉ )
Storage Temperature
-25~60 ℃ (-13~140 ℉)
IT02S Mini Tof Sensor Module Diagram
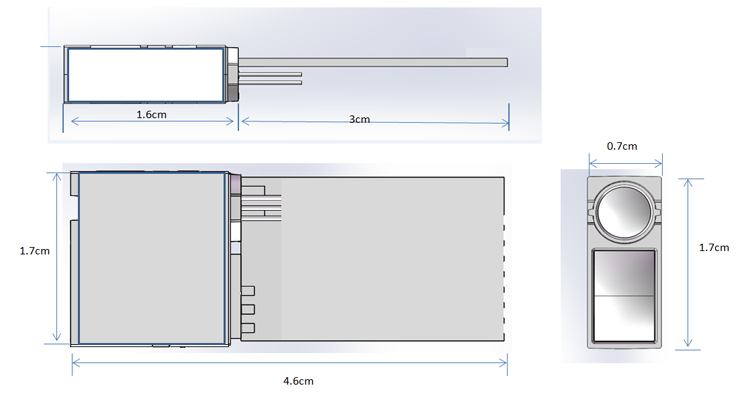
Parameters of IT02S:
IT02S – the High performance-price ratio measurement solution
* low power consumption of single transmit and single receive
* small size: 46*17*7mm
* low cost
* proffessional techinical support
2D Laser Distance Sensor,2D Lidar Sensors,Tof Lidar Distance Sensor, Flight Distance Sensor
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.cdlaserdistancemodule.com