Primary culture of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) can be: (1) for cell conservation; (2) for molecular biology research; and (3) for gene therapy related research.
experimental method
- Trypsin digestion 1
- Trypsin digestion 2
| Principle of experimental method | Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) were taken out from the body, treated with trypsin, chelating agent (usually EDTA), dispersed into single cells, and cultured in MEF growth medium to allow cells to survive, grow and multiply. |
|---|---|
| Experimental Materials | Pregnant rat |
| Reagents, kits | PBS EDTA trypsin MEF growth medium FBS high glucose DMEM |
| Instruments, consumables | Ophthalmology Direct Cut Ophthalmology Straight Ophthalmology Curved Glass Plate 3 Nylon Filter Centrifugal Tube Surgical Blade |
| Experimental procedure | First, the preparation of experimental materials Animal Pregnant mice (mouse) between 14 and 16 days of pregnancy. 2. Reagent Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ free PBS (D-PBS), 0.05% trypsin, 0.53 mmol/L EDTA solution, MEF growth medium (high glucose DMEM plus 10% FBS). 3. Apparatus 3 ophthalmic direct cuts, 3 ophthalmology straights, 2 ophthalmic bends, 3 sets of glass plates, 200 mesh nylon strainers, 50 ml and 15 ml centrifuge tubes and surgical blades. All of the above items require autoclaving. Second, the specific operation 1. Kill the pregnant rat, soak it in 75% alcohol, then cut the skin of the pregnant mouse with scissors and tweezers in a clean bench, cut the abdominal muscle layer with another set of scissors and forceps, expose the uterus, and finally use the first Three sets of scissors and forceps were carefully removed from the uterus and placed in a glass dish containing D-PBS, and rinsed to remove blood. 2. Carefully remove the extracellular membrane with two curved tweezers, then clip the head and internal organs, transfer the remaining embryos to a 50 ml centrifuge tube containing 30 ml D-PBS, gently invert twice, and drain D-PBS, repeat this step once again, taking care to leave a little D-PBS, then transfer the embryos to another dish containing D-PBS and finely chop it with a surgical blade. 3. Using a 200 μl pipette, repeatedly and quickly blow the liquid from the plate, transfer to a 15 ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 1500 rpm for 5 minutes at 4 ° C, pour off the supernatant, and resuspend the pellet with 10 ml of trypsin. Digested in a 37 ° C water bath for 30 minutes, and gently shake every five minutes to fully digest. 4. Pour the supernatant cell suspension into a 50 ml centrifuge tube containing 10 ml of MEF growth medium, filter with a 200-mesh nylon mesh, centrifuge at 5 500 rpm for 5 minutes, and grow with 30 ml MEF. The base was washed twice. 5. The cell pellet was resuspended in 15 ml of MEF growth medium and counted for cells (typically 2-3 x 10 7 cells were obtained for 8 14-day-old fetuses). 6. 3×10 6 cells were suspended in 15 ml of MEF growth medium and inoculated into 200 ml culture flasks. 7. Replace fresh MEF growth medium after 24 hours. 8. After the cells are full, rinse with D-PBS, then pour and trypsin digestion (this step should not be too long, the author usually does not exceed five minutes), pass 1:5. 9. The cells grow to a coverage of 80-90% again, and after they are digested, they are routinely frozen (the frozen stock solution is ready for use). 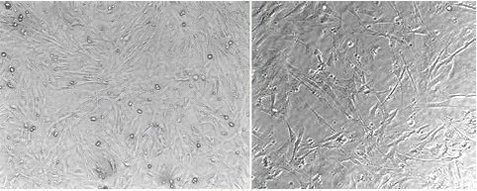  Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF 100 times) |
| Precautions | 1. Primary culture must avoid pollution. 2. The survival ability of MEF is limited. If it is not frozen, it will survive for about ten generations in vitro. 3. Cells that have recovered after cryopreservation can only be passaged once because these cells have limited reproductive capacity. 4. Do not digest cells for too long. |
Garden Supply Store,Indoor Gardening Supplies,Landscape Supplies,Magic Garden Supplies
Changzhou Satidi Import and Export Co., Ltd. , https://www.guanjiejt.com