Sensitivity of DNA methylation site detection using high resolution melting curves on LightScanner
introduction
DNA methylation is an important form of epigenetic CpG dinucleotide modification, and abnormal DNA methylation patterns occur in CpG islands of many gene promoters, which increases the risk of cancer. Hypermethylation of CpG islands often leads to gene silencing, which is closely related to cancer, aging, gene imprinting, and X-chromosome inactivation. In addition, whole-genome CpG hypermethylation has also been confirmed in the early stages of tumor formation. The traditional method for detecting methylation sites is by bisulfite treatment, after treatment, the promethylated cytosine is retained, and the non-methylated cytosine is converted to thymine, which is then directly sequenced. The methylated cytosine is not altered and is therefore readily identifiable by sequencing. In this study, our system evaluated the reliability of methylation detected by LightScanner's high-resolution dissolution profile. If this method is reliable and sensitive in detecting methylation, the tedious process of sequencing can be reduced.
Untreated and SssI-treated pBluescript II SK(+) plasmids were bisulfites using the Qiagen EpiTect kit. Samples are fully methylated and sulfite treated by sequencing specific regions. The primers were designed to amplify 7 different fragments containing 1-8 CpG sites with a fragment size of 79-216 bp. 100% methylated and unmethylated samples are mixed at 50%, 40%, 30%, 20%, 15%, 10%, 5%, 2%, 100% methylated and unmethyl The based samples can be clearly distinguished. When the two samples were mixed in the above ratios, the melting curve exhibited a repeated dose-display relationship, with the 50% mixing being the most biased with the unmethylated standard. The sensitivity of the high-resolution dissolution profile is sufficient to detect methylation sites, with a sensitivity of 2% for small fragments and 10% for large fragments.
Important DNA methylation sites are shown in B lymphoproliferative disorders such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). External silencing of tumor suppressor genes can be altered by treatment with DNA methylation inhibitors. In this study, the upstream methylation site of the CpG island of miR-195 gene in CLL patients was treated with Vidaza or Cladribine, and the highest resolution of CpG methylation changes by bisulfite treatment was performed by PCR amplification, followed by high resolution with LightScanner. Solubility curve analysis. The samples were converted to different cytosines after sulfite treatment and then analyzed for sensitivity by separation and mixing. Any intentionally retained C between different clones can be distinguished in heterologous or homologous mixed samples. This result confirms that the high resolution melting curve is a simple and highly sensitive method for detecting methylation sites.
Figure 1: 2.9 Kb of pBluescript CpG methylated using Sssl methylase. Both methylated and unmethylated samples were subjected to bisulfite treatment using the Qiagen EpiTect Kit, followed by PCR amplification, Lightscanner detection, and finally by sequencing.
Figure 1A: Four fragments of 100% methylated and 100% unmethylated bisulfite treated.
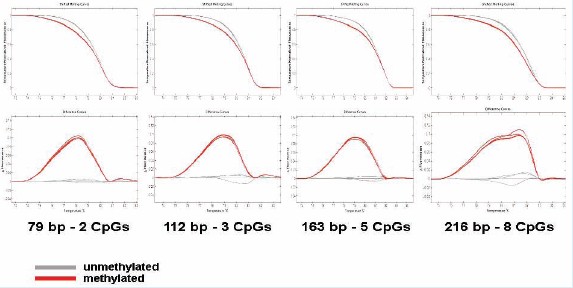
Figure IB: 79-216 bp methylated and unmethylated fragments with 2-8 CpG sites were mixed in different ratios. The sensitivity for detection of small fragments with less CpG is 2%, and the sensitivity for detection of large fragments with more CpGs is 10%.
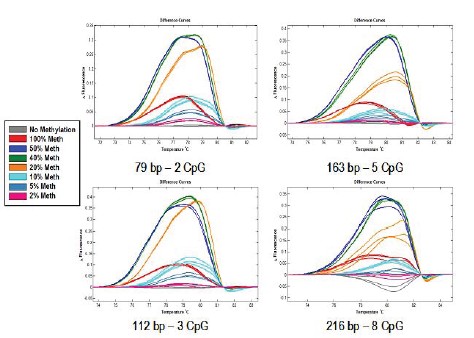
Figure 1C: 110 bp containing one CpG site, methylated and unmethylated samples were mixed in different ratios. (8 repetitions)
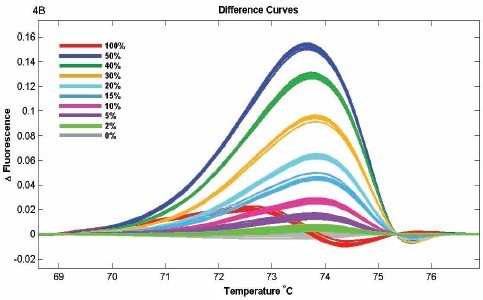
Figure 2: Methylation inhibitor treatment of patients with CpG islands
The following figure shows the changes of upstream CpG island methylation sites of microRNA195 (269bp) before and after treatment with methylation inhibitor Vidaza or Cladribine.
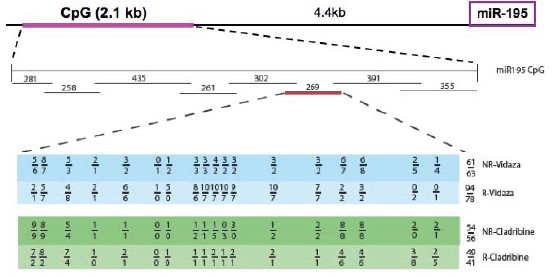
Figure 3: 269 bp amplified region of miR-195 CpG island
![]()
The CpG sites of two different patients are shown in the table below.
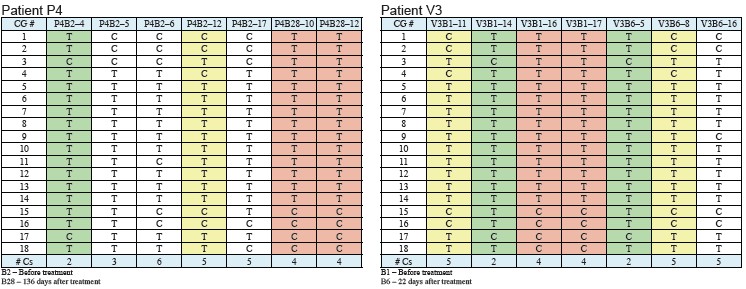
Figure 4: 150bp amplification region of miR-195 CpG island
![]()
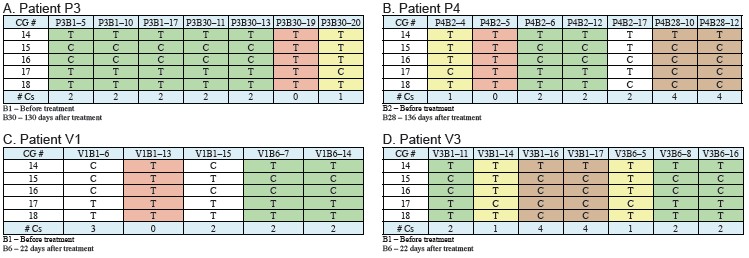
Figure 5: The possible regulatory region of miR-195 was cloned from 4 CLL patients, subjected to bisulfite treatment using Qiagen EpiTect Kit, followed by PCR amplification, Lightscanner detection, and sequencing. Different patients took different methylation pattern amplifications (0-8 Cs). The melting curve is a 269 bp fragment (A) containing an 18 CpG site and a 150 bp fragment (B) containing a 5 CpG site.
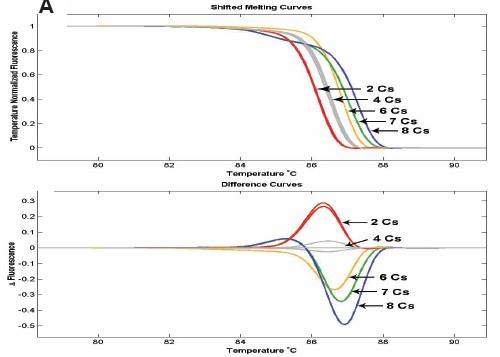

Figure 6: Cloning of different methylation patterns in different patients was performed in equal amounts, and a 150 bp fragment containing 5CpG was amplified. Comparison of methylation and unmethylation control before and after methyl inhibitor treatment, the melting curves were patients P3 (A), P4 (B), V1 (C), V3 (D), respectively.
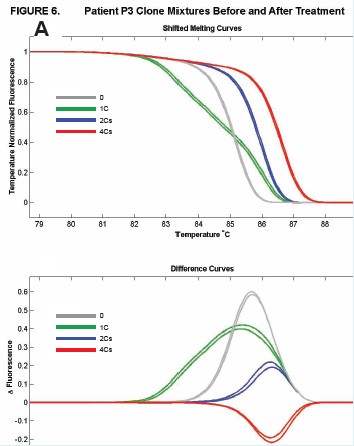
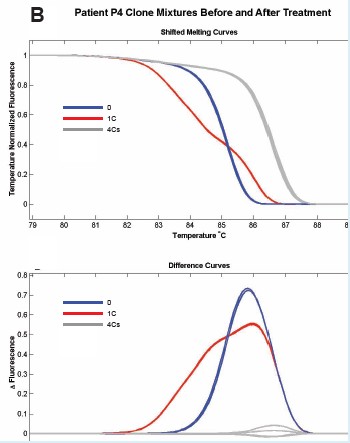
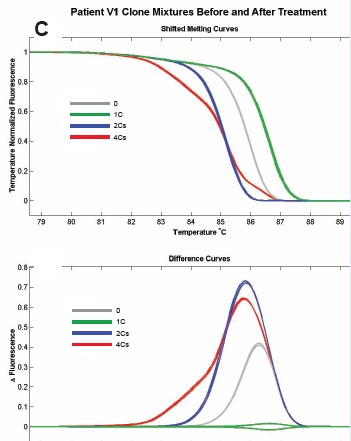
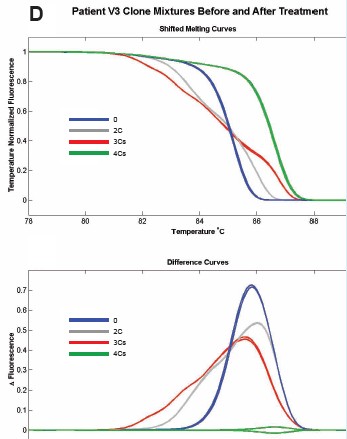
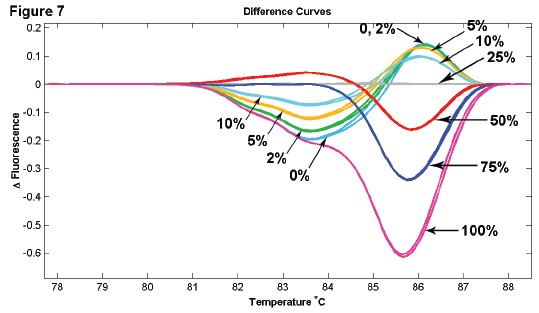
Figure 7: Methylated and unmethylated DNA samples were mixed in different ratios, and the 150 bp fragment contained 5 and CpG sites.
to sum up
Different DNA methylation patterns were used to evaluate the ability of the LightScanner high resolution melting curve. The use of plasmids to control 100% methylated and unmethylated fractions showed a dose relationship, with 50% mixing and maximal deviation from unmethylation. The analysis showed that the sensitivity of the methylation detection of small fragments was 2%, and the sensitivity of large fragments was 10%.
In the CLL assay, the methylation site of the patient's miR-195 gene CpG island was detected after treatment with a methyl inhibitor. Any intentionally retained C between different clones can be distinguished in heterologous or homologous mixed samples. The conclusion confirms that the use of high resolution dissolution profiles is a simple and sensitive method for detecting methylation sites.
Mosquito Repelling Lamp, Mosquito Repellent Lamps
Ningbo Sunfine UV lighting Co.,ltd. , http://www.uvlightings.com