Foreword
Impurity analysis is critical for drug development1. During the course of the study, impurity profile information can help drug chemists optimize synthetic routes and avoid potentially toxic impurities. In the development process, the identification and characterization of trace impurities is essential when a large amount of parent compound is present, which promotes the development of HR-MS instruments and intelligent structure identification software with high resolution, high sensitivity and high scanning speed.
In order to demonstrate the ability of HR-MS in impurity analysis and structure identification, the commercially available drug omeprazole was selected in this paper. This study used Thermo Scientific's Q Exactive Focus benchtop Orbitrap mass spectrometer and data processing software Mass Frontier to quickly analyze and identify the structure of impurities in omeprazole.
method
Materials and reagents
Omeprazole (CAS# 73590-58-6) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Product number O104-100MG.
Acetonitrile and water from Fisher Scientific
Ammonium acetate was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, product number 73594-25G-F.
Formic acid was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, product number 33015-500 ml.
Sample preparation
Omeprazole solution (0.5 mg/mL) was prepared in a 1:1 acetonitrile/water mixture.
HPLC method
The chromatographic separation was performed using a Thermo Scientific Ultimate 3000 UHPLC system.
Column: Thermo Scientific Hypersil GOLD column, 2.1 mm x 150 mm, particle size 3 μm.
Column temperature: 35 °C, flow rate: 0.5 mL/min, injection volume: 8 μL
Mobile phase: A - water; B - acetonitrile; C - 100 mM ammonium acetate, adjusted to pH 5 with acetic acid
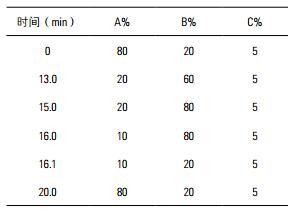
Gradient elution:
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry was performed using an electrospray positive ion mode from a Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Focus mass spectrometer. High-resolution full-scan first-order mass spectral data and data-dependent secondary mass spectral data were acquired at 70,000 and 35,000 resolutions of FWHM@m/z 200, respectively.
Ion source conditions:
Ionization mode: positive ion ESI
Ion source: HESI-II
Sheath gas flow rate: 45 units N2
Auxiliary gas flow rate: 10 units N2
Spray voltage (KV): +3.5
Capillary column temperature (°C): 320
S-lens RF Level: 50.0
Heater temperature (°C): 400
Q Exactive Focus method parameters:
AGC target (full scan): 3e6
AGC target (MS/MS): 1e5
Collision energy: 30, 35% step change scan range (full scan MS): 180 to 1200 amu
Results and discussion
I. High Resolution Full Scan - HCD MS/MS Identification of Impurities
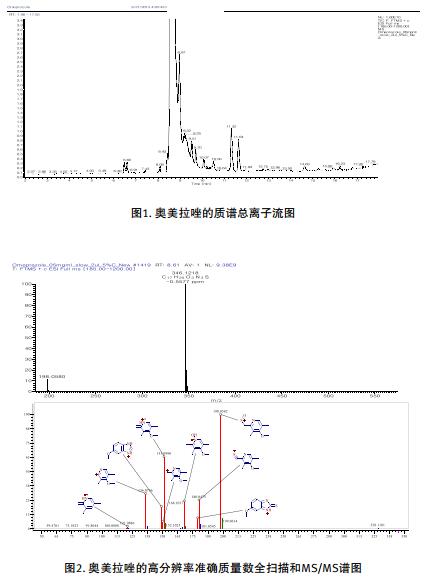
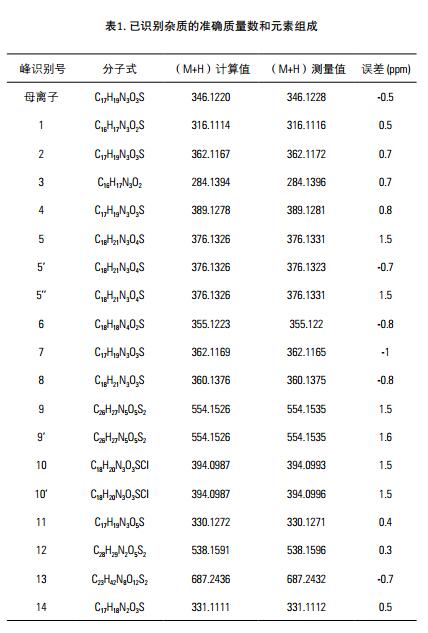
The high-resolution full scan of the omeprazole and the three highest intensity data were relied upon for HCD MS/MS data. HRAM full scan and MS/MS data provides molecular weight and fragmentation information. HCD (High Energy Collision Dissociation) yields rich MS/MS fragmentation and low quality end fragmentation information. Using Mass Frontier software to work with this information, we not only quickly detected the major impurities of omeprazole, but also reliably determined the corresponding elemental composition, as shown in Figure 1 & 2 and Table 1.

II. Mass Frontier for structural identification of unknowns
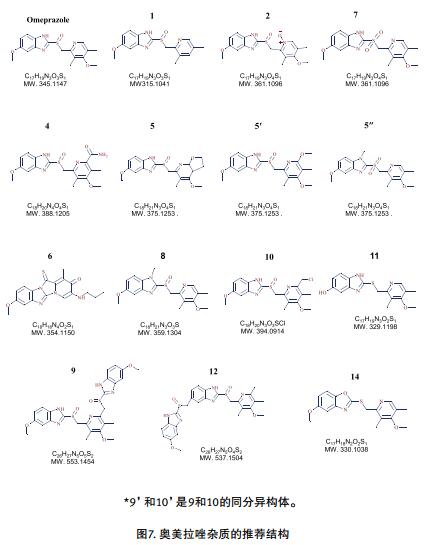
The HRAM full scan and MS/MS data is processed using Mass Frontier's Fragment Ion Search (FISh) function, as shown in Figure 3-a. FISh can easily identify compounds with the same fragment ions as the parent compound, see Figure 3-b, and infer the possible impurity structure from the fragments, see Figure 7. By searching Mass Frontier's HighChem spectrum database, Mass Frontier's Fragment and Mechanism feature provides a reference for recommended structures. The “Fragment and Mechanism†results for each recommended structure provide a good help in understanding the source of the structure. Comparing the data results with "Fragment and Mechanism" provides more confirmation/negative criteria for the proposed structure.
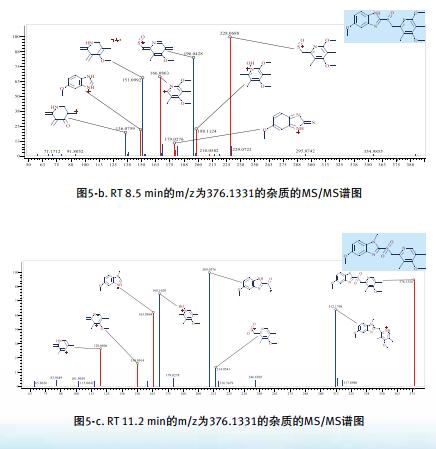
Another important feature of Mass Frontier is the "Annotation Map of the Fragment Structure" for automatic prediction of debris. The structural identification of the three isomers demonstrates this function, see Figures 4 and 5.

in conclusion
The Q Exactive Focus benchtop Orbitrap system enables high-resolution accurate mass determination (HRAM) of full scan and MS/MS data, providing critical molecular weight and structural information for structural identification of unknown impurities: HRAM Full scan for accurate determination of elemental composition HRAM MS/MS can accurately determine the impurity composition.
The Mass Frontier Fragment Ion Search (FISh) and Fragment and Mechanism functions accurately identify the structure of an unknown by searching the HighChem Fragment Database.
A workflow consisting of Q Exactive Focus HRAM data and Mass Frontier software helps researchers efficiently and accurately identify impurities in each batch of API early in drug research.
references
1. FDD Guidance for Industry, Q3A (R2) Impurities in New Drug Substances
One Button Fast Measuring Instrument Horizontal Type
One-button flash tester (horizontal) :
â‘ Fast: multiple products can be measured at the same time. After the products are placed, the dimensions of multiple products placed on the platform can be measured with only one key, which subverts the traditional measurement mode.
No human error: anyone's measurement results are the same.
â‘¢ Simple: anyone can easily and quickly operate.
(4) Random: products can be placed at will, without any fixture.
⑤ The data report can be automatically exported after the measurement.
The appearance of the integrated design, generous, beautiful. The fuselage main frame adopts the combination of high standard aviation aluminum and granite to ensure the stability of the equipment.
⑦ Powerful software processing system and accurate algorithm, to obtain high precision measurement results.

One Button Fast Measuring Instrument Horizontal Type,High Precision Fast Detector ,Fast Detector ,Fast Splicing Detector
Zhejiang dexun instrument technology co., ltd , https://www.dexunmeasuring.com