Foreword
Forced degradation experiments can reveal the effects of various environmental factors on the drug substance and formulation. It provides drug safety information, determines recommended storage conditions, shelf life, and specificity of analytical methods. Information on degradation products can help improve the development of compounds or formulations.
Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) is trade name for CellCept and is a prodrug of immunosuppressant and mycophenolic acid (MPA). MMF is widely used in the treatment of transplants for organ transplant rejection and autoimmune diseases. This study selected MMF as a model compound.
This paper develops a complete workflow A fast and reliable analysis of mycophenolate mofetil degradation products, instruments using the Thermo Fisher Scientific's Accela TM
UHPLC system and benchtop Orbitrap Q Exactive FocusTM mass spectrometer with data processing using Mass FrontierTM software. The pH values ​​of the degradation of mycophenolate mofetil under thermal and peroxide catalysis were set at 2.0, 3.5, 6.0 and 8.2. Rapid identification of degradation products in high resolution and polarity switching modes using HRAM full scan and data dependent MS/MS. HRAM MS and MS/MS spectra and positive/negative ion mode switching reliably verify the qualitative and structural identification of degradation products.
experimental method
Materials and reagents
Mycophenolate mofemate API CAS# 128794-94-5 was purchased from 2A PharmaChem (Lisle, IL) with a purity of >98%.
Mycophenolate degradation product standard
Mycophenolic acid, CAS# 24280-93-1 Sigma-Aldrich.
Mycophenolate Impurity G, CAS# 224052-51-1, Molcan Corporation, Toronto, Canada, Mycophenolate Impurity A, CAS# 1322681-36-6, Molcan Corporation, Toronto, Canada, hydrochloric acid, ammonium acetate, sodium hydroxide and Hydrogen peroxide was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Sample preparation
â— Mycophenolate stock solution, 2.5 mg/mL acetonitrile solution, weighed 25 mg standard in 10 mL acetonitrile.
• Hydrochloric acid (0.01 N, pH 2), ammonium acetate (5 mM, pH 6), sodium hydroxide (0.01 N, pH 8) and hydrogen peroxide (3%, pH 8.2). The purchased 30% hydrogen peroxide was diluted 10 times with water and used for acid, base and oxidation studies. The pH of the forced degradation solution is adjusted with ammonium hydroxide or acetic acid.
◠Dilute the mycophenolate stock solution at a concentration of 2.5 mg/mL by a solution of pH 2, pH 6, pH 8 and hydrogen peroxide (3%, pH 8.2) to prepare a concentration of 0.25 mg/mL. Degradation solution. The forced degradation solution was placed in an oven at 60 °C. Samples were taken at 1, 20, 48, and 72 hours of placement and injected directly into the LC/MS for analysis.
HPLC method
HPLC System: Thermo Scientific Accela 1250 pump, Open Accela Autosampler and Accela PDA
Column: Thermo Scientific Dionex Acclaim 2.1×150 column, 2.2 μm
Column oven temperature: 35 ° C
Mobile phase: A - 0.1% aqueous formic acid B - Acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid C - 100 mM aqueous solution of ammonium formate (pH 5)
Gradient elution: 0-0.5 min Maintain 20% B and then linearly increase to 40% B in 15 min
Flow rate: 500 μL/min
Injection volume: 1 μL
Mass spectrometry
Mass Spectrometer: Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Focus benchtop high resolution mass spectrometer with HESI-II ion source ionization mode: ESI positive/negative ion switching full scan acquisition: m/z 120-1000 amu, resolution 70,000 (FMHW@m/ z 200)
MS/MS acquisition: Response intensity data dependent acquisition at 35,000 resolution
HCD collision energy: 35%, 25% step change
Results and discussion
I. UHPLC- High Resolution MS Rapid Determination of Degradation Products
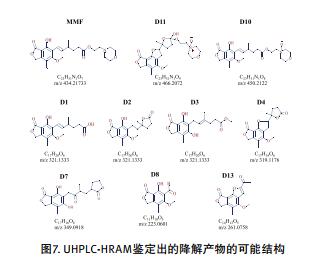
The degradation products were analyzed rapidly using UHPLC-high resolution MS. The high-quality HRMS full-scan map provides important information for determining the elemental composition of the degradation products, and the subsequent data is dependent on MS/MS to obtain molecular ion cleavage information.
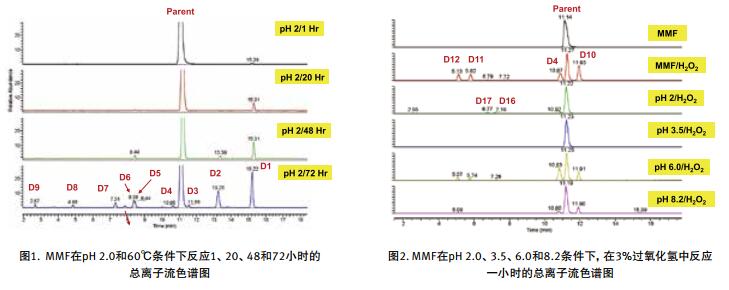
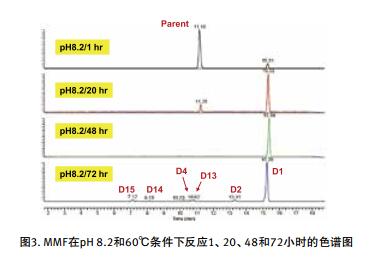
II. Identification of degradation products by high resolution MS/MS
The high-resolution and high-energy collision dissociation function with stepped collision energy produces information-rich fragments, which can more easily complete the structural identification of degradation products.
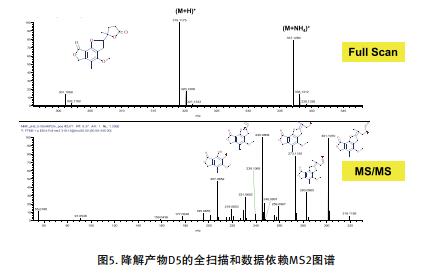
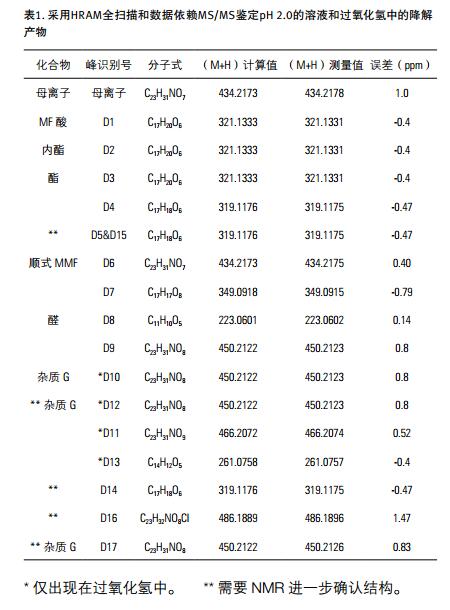
III. Polarity switching function comprehensively identifies degradation products
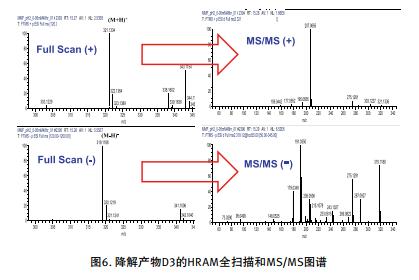
The fast positive/negative ion switching experiment uses a full scan in positive ion mode followed by data dependent MS2 HCD cleavage. Subsequent conversion to negative ion mode for full scan and data dependent MS2 HCD cleavage. Automatic polarity switching provides cleavage information for different but complementary supplements. These uniquely polar fragments can help confirm structural identification results (Figure 6).
in conclusion
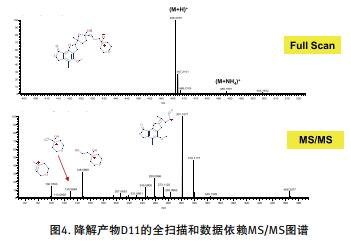
In this paper, the thermal and hydrogen peroxide degradation of mycophenolate API at pH 2.0, 3.5, 6.0 and 8.2 was investigated. Rapid and accurate analysis of degradation products was performed using a desktop high resolution mass spectrometer Q Exactive Focus in conjunction with a UHPLC system, see Figures 1, 2 and 3.
• High-resolution accurate mass measurement (HRAM) full-scan map enables rapid identification – obtaining key information on the composition of the degradation products.
• A highly informative high-energy collision dissociation (HCD) MS/MS map facilitates the accurate identification of degradation products.
â— The positive/negative ion switching mode in full scan and MS/MS mode fully identifies degradation products, as shown in Figures 4 and 5.
â— Data analysis software Mass Frontier greatly improves the speed and reliability of structural analysis of degradation products.
The Q Exactive Focus benchtop Orbitrap MS delivers powerful capabilities to quickly and efficiently perform degradation product analysis on an integrated UHPLC/HR-MS/MS platform, significantly increasing the identification flux of degradation products during drug development.
references
1. M. Brandl, Degradation Products of Mycophenolate Mofetilein Aqueous Solution Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 25 (3), 361-365 (1999)
2. FDA Guidance for Industry. Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation (draft guidance), August 2000.
3. ICH guidelines Q1A (R2). Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products (revision 2), November 2003.
Cervical Tractor,Tractor Cervical,Cervical Vertebra Tractor,Cervical Traction Tractor
Hebei Dingli Medical Apparatus and Instrument Co., LTD , https://www.dinglimed.com