Liu Guoqiang
Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd.
Key words
Brazilian propolis; liquid chromatography; mass spectrometry; isodecadienyl cinnamic acid derivatives
Summary
A reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography-ion trap electrostatic field orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) method was developed for the simultaneous determination of 27 active compounds in Brazilian propolis. The experimental results show that ethanol:water (8:2) extracts more phenolic components than ethyl acetate: methyl tert-butyl ether (1:1) and methyl tert-butyl ether: methanol (9:1). . A total of 27 components were identified from Brazilian propolis by multi-stage mass spectrometry obtained from Orbitrap Elite, containing 11 flavonoids, 15 phenolic compounds, and 1 organic acid compound. Among them, isodecadienyl cinnamic acid derivatives are an important physiologically active ingredient in Brazilian propolis. Artepillin C and Drupinin identified in this experiment can be used as markers for quality control of Brazilian propolis. Object. This analytical method can be used for the analysis of the chemical composition of propolis and the quality identification of commercial Brazilian propolis products.
introduction
Propolis is a kind of resin in which the honeybee collects the rubber-derived plant and the secretion of the upper parotid gland and wax gland. It is repeatedly processed by the bees to the entrance and inner wall of the hive to keep the colloidal substance in the nest relatively sterilized. It is a rare species. , precious bee products. Propolis has many active functions, such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic, cholesterol lowering, and anti-tumor. The main active ingredients in propolis are flavonoids and phenolic compounds, as well as chemical components such as fatty acids, amino acids, terpenes, minerals, vitamins and trypsin.
Brazilian Bee Propolis refers to propolis produced in Brazil. Its appearance and composition are quite different from propolis in other parts of the world. Isoprene is abundant in propolis in southeastern Brazil, and isoprenyl cinnamic acid derivatives are pharmacologically active in Brazilian propolis, four of which are benzopyrene with isoprene heterocycle. Norm, Brazilian propolis is sought after by the world's propolis industry because it contains a special ingredient of “Artiline Câ€, which is known as “the world propolis looks at Brazilâ€.
With the rapid development of propolis industry, propolis is widely used in medicine, food, cosmetics and other fields. The content of main active substances such as ferulic acid and phenethyl ethyl acrylate in propolis also directly affects the physiological activity of propolis. The use of flavonoids alone to control the quality of propolis is no longer sufficient. Therefore, comprehensive and comprehensive analysis of the chemical composition of propolis is of great significance for establishing the fingerprint of propolis and evaluating the quality of propolis. In this paper, the chemical composition of propolis capsule samples from Brazil was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography-ion trap electrostatic field orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. Under optimized liquid conditions, Obitrap Elite was used in the sample. The exact molecular weight of each chromatographic peak was determined, and the only possible elemental composition was fitted within the mass deviation range of 1 ppm. Combined with the fragmentation rule of multi-stage mass spectrometry and database screening, a total of 27 were identified from Brazilian propolis. The main ingredients.
1. Experimental Methods
1.1 reagent and sample preparation
Methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, methyl tert-butyl ether, and acetonitrile (chromatographically pure, Merck, Germany), formic acid (super pure, Merck); sample of Brazilian propolis capsules, finely ground, weighed 0.5g Add ethanol: water (8:2), ethyl acetate: methyl tert-butyl ether, or methyl tert-butyl ether: methanol, ultrasonic extraction for 30 minutes, using 0.22 μm microporous membrane After filtration, direct injection analysis.
1.2 liquid chromatography conditions
Instrument: Dionex UltiMate 3000 LC
Column: Thermo Scientific Syncronis C18 (150 x 2.1 mm, 5 μm)
Mobile phase gradient: A is the aqueous phase: 0.1% formic acid water, B is the organic phase: acetonitrile
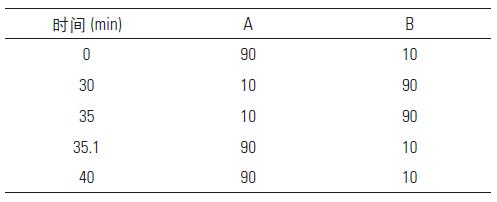
The flow rate was 0.35 mL/min, the injection volume was 2 μL, the detection wavelength was 254 nm, and the column temperature was 30 °C.
1.3 mass spectrometry conditions
Instrument: Thermo Elite Dual Pressure Linear Ion Trap - High Resolution Electrostatic Field Orbitrap Combined Mass Spectrometer
Mass spectrometry parameters: HESI Spray voltage: +3.5KV/-3.0KV; Sheath Gas Pressure: 35arb; Aux Gas Pressure: 10arb; Capillary Temp: 320 °C;
Heater Temp: 300 ° C; Scan mode: Full MS (Resolution 60,000), and MS 2-5 (Resolution 17, 500, NCE 30); Scan range: m/z 100~1000.
2 . Experimental result
2.1 Comparison of different extraction solvents for Brazilian propolis samples
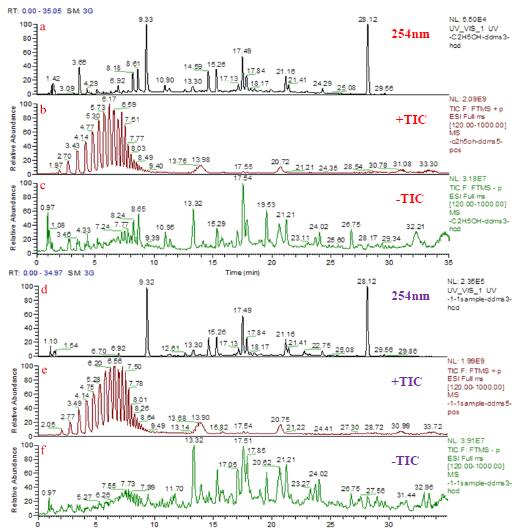
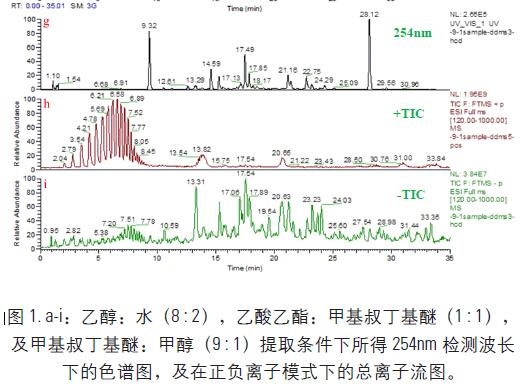
The composition of propolis in Brazil is complex. It is difficult to separate the various components in propolis by isocratic elution. Therefore, the propolis fraction is separated by gradient elution. Under the selected chromatographic conditions, the extraction efficiency of the active components in the propolis was investigated by different extraction solvents. The chemical components in the sample were extracted with ethanol: water (8:2), ethyl acetate: methyl tert-butyl ether (1:1), and methyl tert-butyl ether: methanol (9:1). The resulting chromatogram at the 254 nm detection wavelength and the total ion chromatogram (TIC) in positive and negative ion mode are shown in Figure 1. From the UV absorption chart, it can be seen that ethyl acetate: methyl tert-butyl ether (1:1) and methyl tert-butyl ether: methanol (9:1) have similar sample compositions, ethanol: water (8: 2) Some peaks appeared before 9 min.
2.2 Identification of chemical constituents in Brazilian propolis samples
It can be seen from the above that the chemical composition of propolis is more efficiently extracted under the condition of ethanol:water (8:2). Figure 2 is the chromatogram of the sample at the detection wavelength of 254 nm under the extraction conditions, and in positive and negative ion mode. The total ion chromatogram (TIC) is shown below. It can be seen that the chemical composition of the sample has a good response under the ESI negative ion mode, and the positive ion mode is greatly inhibited by the interference of the polyethylene glycol. The 1-27 indicated in the ion chromatogram is the main component identified in the propolis.
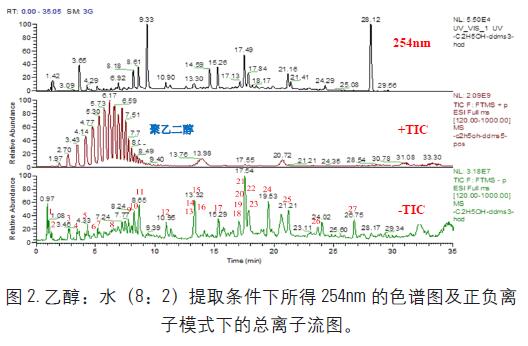
In positive ion mode, a series of peaks with strong response were observed before 10 min, and the first-order mass spectrum of the peaks at 1.97, 2.70, 3.43, and 4.14 min is shown in Figure 3:
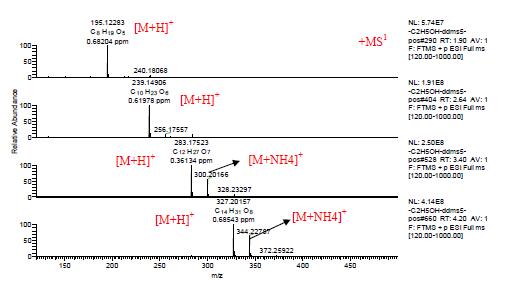
Figure 3. First-order mass spectrum of peaks at 1.97, 2.70, 3.43, and 4.14min in ESI positive ion mode.
[M+H]+ m/z 195.12283, 239.14906,283.17523, and 327.20157, in the positive and negative ion mode, with C, H, O, and N within 1 ppm deviation range, fitting the element composition from the first-order mass spectrum. The only elemental composition is C8H19O5, C10H23O6, C12H27O7, and C14H31O8. The four-peak molecular formula is C2H4O, which should be a polyethylene glycol compound.
As shown in Figure 4 below, in the positive ion mode, the secondary mass spectra of [M+H]+ m/z 195.12283, 239.14906, 283.17523, and 327.20157 show that the main fragment ions are fragment ions obtained by losing C2H4O or H2O. It is known from the fragment ion m/z 89.05966 that the terminal group of this polyethylene glycol is a hydroxyl group. Therefore, it can be seen that a series of compounds appearing in positive ion mode is polyethylene glycol HO(CH2CH2O)nH, which is an excipient component in a sample of Brazilian propolis capsules.

Figure 4. Secondary mass spectrum of [M+H]+ m/z 195.12283, 239.14906, 283.17523, and 327.20157.
The multistage mass spectra of components 9, 10 and 11 are shown in Figures 5, 6, and 7, and [MH]- m/z 515.11859 is visible in negative ion mode. In the negative ion mode, C, H, O, and N are within the range of 1 ppm deviation, and the elemental composition is fitted from the first-order mass spectrum, and the molecular formula is C25H24O12, and the three are isomers.
In the negative ion mode, the secondary mass spectrum of the components 9, 10 and 11 [MH] - m/z 515.11859 shows that the main fragment ion is the base peak ion m/z 353.08694 obtained by losing the caffeoyl C9H6O3; in the third-order mass spectrum It can be seen that the main fragment ions of m/z 353.08694 are the fragment ion m/z 191.05588 obtained by losing caffeoyl C9H6O3, the fragment ion m/z 179.03482 obtained by losing quinic acid C7H10O5, and the fragment ion m/z 173.04544 obtained by losing caffeic acid C9H8O4.
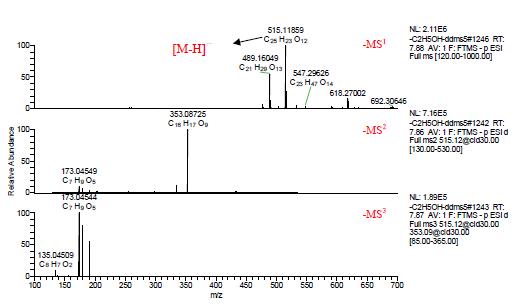
Figure 5. Component 9 Multistage mass spectrum in ESI negative ion mode.
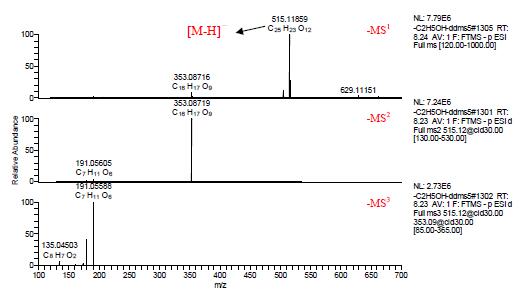
Figure 6. Multi-level mass spectrum of component 10 in ESI negative ion mode.
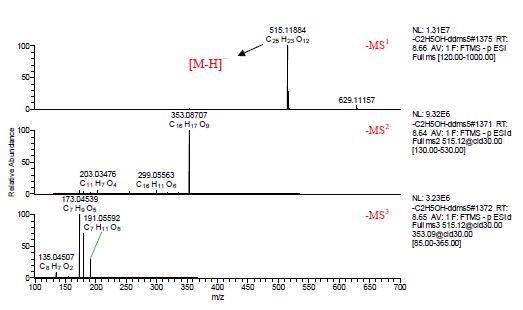
Figure 7. Component 11 Multistage mass spectrum in ESI negative ion mode.
For the 10th, the tertiary mass spectrum contains the characteristic base peak ion m/z191.05588. For the components 9 and 11, the characteristic fragment ion m/z173.04544 is the base peak ion, and the relative abundance of the fragment ion It can be seen that the components 9, 10 and 11 are 4,5-di-caffeoquinic acid 4,5-di-O-caffeoyquinic acid; 3,5-dicaffeoquinic acid 3,5-di-O-caffeoyquinic acid And 3,4-dicaffeoquinic acid 3,4-di-O-caffeoyquinic acid.
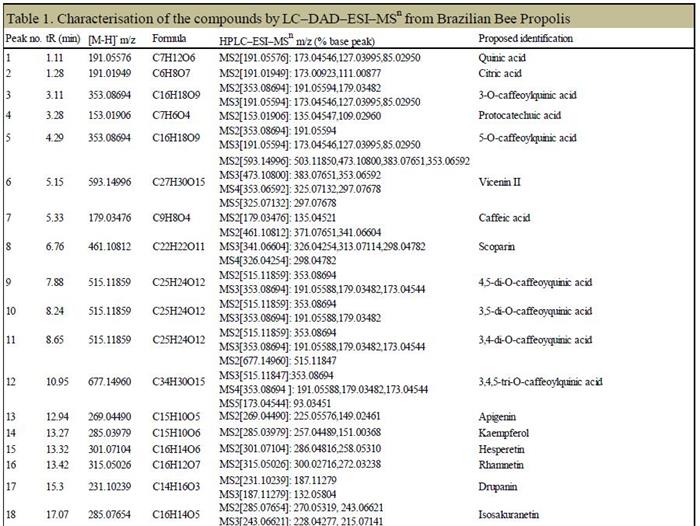
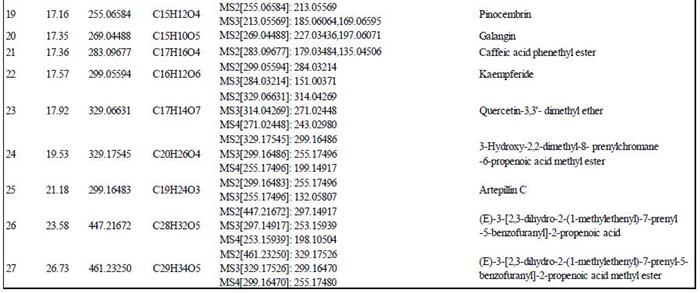
The Obitrap Elite was used to accurately determine the molecular weight of each peak in the sample, and to fit the only possible elemental composition within the mass deviation range of 1 ppm, combined with the fragmentation rule of multi-stage mass spectrometry and database screening. A total of 27 major components were identified in the Brazilian propolis samples. The structure and major fragment ions are shown in Figure 8 and Table 1, respectively.
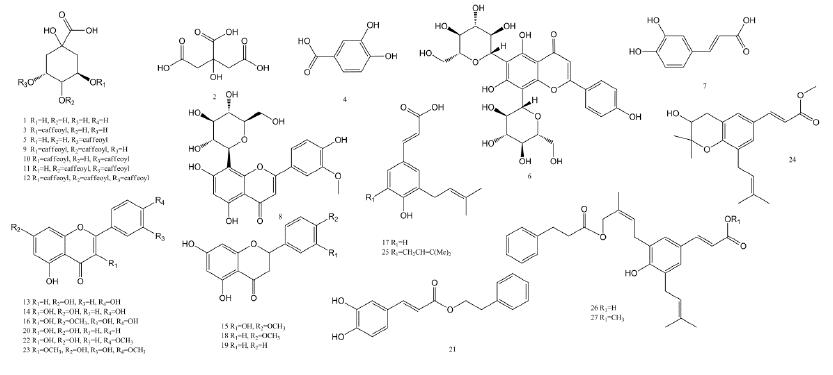
Figure 8. Structural formula of 27 components identified in Brazilian propolis samples.
Table 1. Brazilian propolis-like samples 1. In the sample of Brazil's bee-determined gelatinous samples, 7 of which are determined to be divided into 2, and the 7 main components of which are divided into the main broken pieces are separated from the broken pieces. And the name of the compound and the compound.
3 Conclusion
3.1 The Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Elite mass spectrometer combines a dual pressure linear ion trap with high resolution accurate mass (HR/AM) Orbitrap detection technology to deliver superior performance and versatility. Its multi-stage mass spectrometry MSn ability contributes to the identification of isomers, such as 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, and 3,4-di in this experiment. For caffeoylquinic acid, it can be distinguished by the relative abundance of fragment ions in the three-stage mass spectrum.
3.2 The ethyl acetate: methyl tert-butyl ether (1:1) and methyl tert-butyl ether: methanol (9: 1) were extracted in the same sample. Ethanol: Water (8: 2) appeared some phenolic compounds before 9 min, and its extraction efficiency was higher.
3.3 In the case of interference from polyethylene glycol excipients in Brazilian propolis capsule samples, the multi-stage mass spectrometry obtained by Orbitrap Elite still identified 27 main components from the CCP, including 11 flavonoids and 15 phenolic compounds. And one organic acid compound. Artepillin C and Drupinin identified in this experiment can be used as markers for quality control of propolis in Brazil. This analytical method can be used for the analysis of the chemical composition of propolis and the quality identification of commercial propolis products in Brazil.
Dried Garlic Flakes,Fried Garlic Flakes,Slice Of Garlic,Roasted Garlic Slices
shandong changrong international trade co.,ltd. , https://www.cragriculture.com