What have we seen behind the latest precision medical proteome milestones?
Whether it's focusing on professionals in the field of proteomics, outside the field, or even outside the academic circle, I think many people are hard to hide at this moment. On February 28, 2019, the Military Medical Research Institute of the Academy of Military Sciences, the National Protein Science Center (Beijing), the State Key Laboratory of Proteomics, the team of Academician He Fuchu, the team of Professor Qian Xiaohong, and the team of Academician Fan Jia of Zhongshan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University, In the international top academic journal "Nature", "Proteomics identified therapeutic targets of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma" was published, and the results of proteomic research on early hepatocellular carcinoma were published online. For the first time in the world, the study describes the proteome expression profile and phosphorylated proteome map of early hepatocellular carcinoma, and further discovers important targets for precise treatment of liver cancer. The reason why this research is to smash the circle of friends is not only because it is entirely from domestic researchers, but also proves that China's proteomics research is at the top of the international positioning; more importantly, the research is destined to become a proteomics application. A milestone in precision medicine.
Proteomics identified therapeutic targets of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
Original link: https://

The researchers discussed the mass spectrometry data. The front row is the academician He Fuchu, and the left is the researcher Qian Xiaohong. (Hong Nan Photography Academy of Military Sciences for the picture, from CCTV network intrusion)
Let us first review the contents and results of the study:
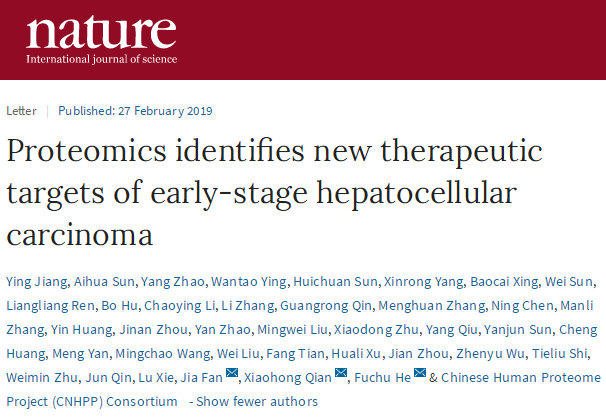
The study collected and selected 101 cancer tissues from patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma and matched paraneoplastic tissue samples. The mass spectrometry-based proteome and phosphorylated proteome technology were used to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the protein and protein phosphorylation of the above samples. The proteome expression profile and phosphorylation of early hepatocellular carcinoma were firstly described internationally. Proteome map.
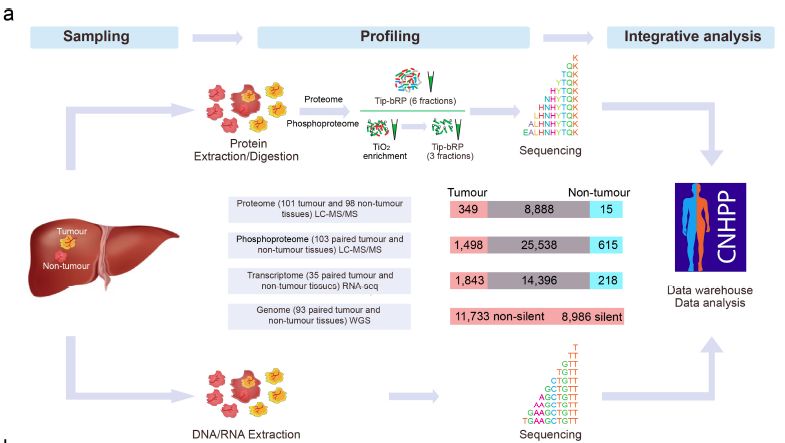
Based on this, the study will divide the clinically considered early stage liver cancer patients into three subtypes of SI, S-II and S-III, and the correlation analysis with clinical data shows that the score The type has clear clinical significance: SI subtype cancer patients only need surgery, should pay attention to over-treatment; S-II subtype patients not only need surgery, but also need to be combined with adjuvant therapy; while S-III subtype has the worst prognosis The risk of recurrence and metastasis is highest after surgery.
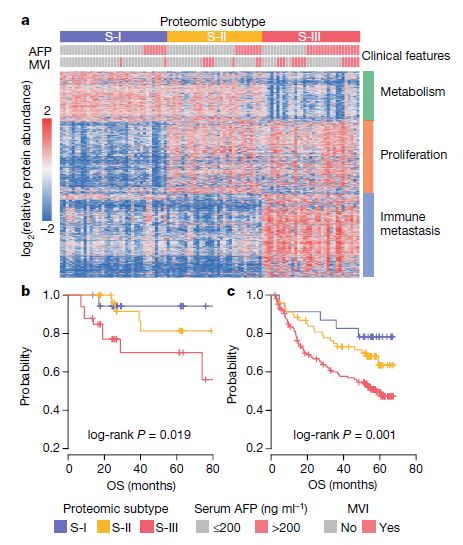
If it is only to map the early liver cancer and provide the corresponding clinical classification basis, the research is not enough to board the top journals, and the significance of clinical treatment will be relatively limited. Further, by mining the omics data, the researchers further revealed the characteristic changes at the signal pathway level, and on this basis, found a key potential therapeutic target - sterol O-acyltransferase (Sterol O- Acyltransferase 1, SOAT1) , its abnormal expression level is highly correlated with prognosis.
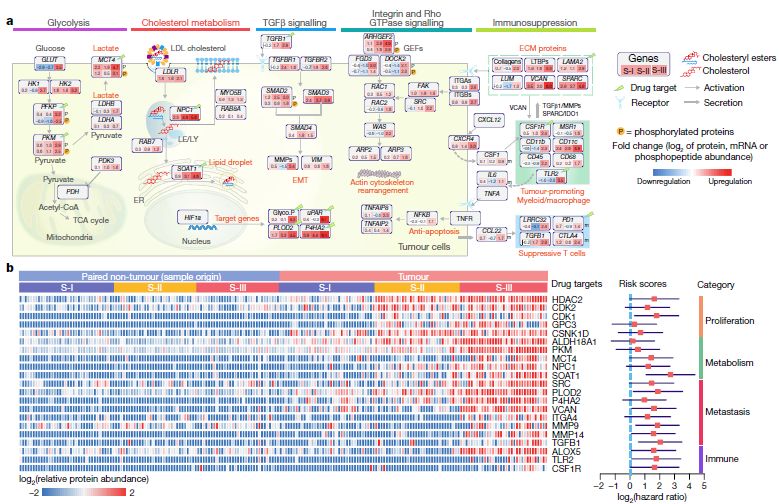
In order to reveal that this molecule may be an important target for tumor drug development, the research team used a human tumor xenograft (PDX) model of liver cancer patients to prove that human inhibitor of SOAT1, avasimibe, is a human tumor in liver cancer patients. The xenograft (PDX) model showed good anti-tumor effect, indicating that arvastat is expected to be an effective treatment for patients with S-III subtype . At the molecular mechanism level, the study further confirmed that SOAT1 gene expression is closely related to the cholesterol intake of cells, and thus participates in the proliferation and migration of tumor cells by affecting the abundance of the molecular integrin family. More broadly, the team also found that SOAT1 protein expression levels were significantly associated with poor prognosis in a variety of tumors (thyroid cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, kidney cancer, and prostate cancer). It is suggested that cholesterol metabolism instability and the cancer-promoting mechanism of SOAT1 are likely to be common mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets in many types of tumors.
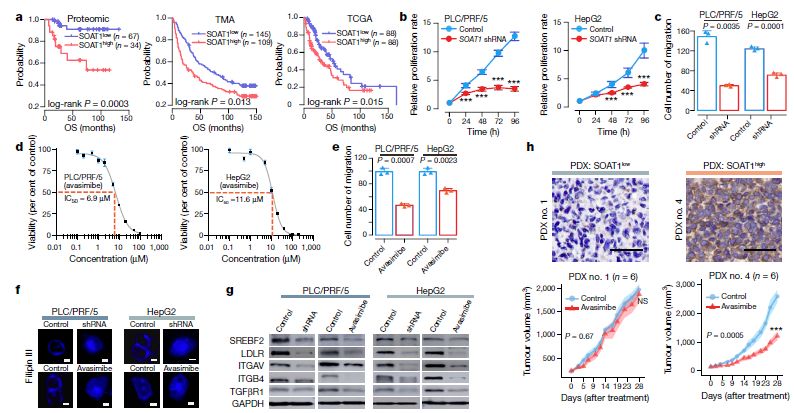
In the above research data and conclusions, as well as its important clinical significance, there may be more significance and value behind the research:
1. Is the tumor a genetic disease?
This is a definition that is relatively clear in academic terms, but may not be completely clear to some extent. The completion of the 2001 draft of the human genome is the starting point. For many years, in the field of cancer, whether in scientific research, clinical diagnosis, clinical treatment, or in the field of bio-industry, the detection of genes and transcription levels is the most popular and indispensable entry point and tool. . Compared to the human genome project known to all, even the researchers in the academic circle know that there are very few sketches of the human proteome in 2014. However, with the completion of the drafting of the human proteome, the situation of genetic testing has changed dramatically. From 2014 to 2018, there have been many outstanding achievements in the "Nature" and "Cell" publications and their sub-publishes. The completed precision typing studies include: endometrial cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer. , ovarian cancer and stomach cancer.

The above research model integrates big data from genome, transcriptome, proteome and post-translational modification groups, redefines disease classification from multi-molecular-level big data, taps potential therapeutic targets, and finally finds at protein level. And to verify tumor-related gene mutations, expression changes and key molecular regulatory mechanisms for more precise drug guidance and drug development, the so-called "Proteogenomics". Fortunately, this model is not only at the research stage: in the same year that the 2016 Cancer Moonshot 2020 was launched, the US VA, DoD, and NCI jointly announced that they will establish the first simultaneous genetic information and protein. The medical system for information characterization uses the genome and proteome as a routine means of detecting individualized protein genomes (Proteogenomics) for cancer patients, providing guidance for more precise medications, the Apollo program . The Apollo Program officially uses Proteogenomics as its core philosophy and working methods .

However, although proteomics are increasingly being valued, the reality is that proteome research still requires “back-to-back†genomes and transcriptomes. Proteomics data must be compared with genes and transcriptions, and more attention is paid to the consistency of the two data, that is, the proteome research on precision medicine has always appeared in the image of “Proteogenomics†rather than “Proteomicsâ€. . In 2018, Professor Qin Wei, also from the above research team, published the "A proteomic landscape of diffuse-type gastric cancer" published in Nature's "Nature Communications", and launched the first "Proteomics" alone. Gun, this study not only provides a basis for accurate classification of diffuse gastric cancer, but also the expression of "abnormal" protein levels and gene level data is also very instructive.

In this study, although the data of gene and transcript level were also analyzed, it can be directly seen from the article name, instead of "Proteogenomics....." but "Proteomics..." , it is the true resistance of the proteome. . I think this is not only important for many proteomics, but also important significance and inspiration for the future development of tumor research, precision diagnosis and precision treatment. It is not difficult to understand from the most fundamental biological level: DNA and RNA are not functional molecules, but proteins are the therapeutic targets of most tumor drugs and the most important clinical diagnostic indicators. Numerous research data currently tell us that the overall correlation between transcriptome and proteome data is not high , whether it is in the field of cancer or other medical fields, or in the field of botany. Although from a technical point of view, there are still many bottlenecks in proteomic level analysis techniques compared to sequencing technologies , protein molecules must be dominant from the point of final biological significance and clinical significance.
2. Still, is the tumor a genetic disease?
Let us explore the issue from another angle. The importance of this study, in addition to guiding the precise typing of early liver cancer, is that it has discovered a cancer-promoting mechanism and potential therapeutic targets - cholesterol metabolism instability and SOAT1 . This extends to another important molecular level - tumor metabolism . Tumor is a metabolic disease, and I think many of the researchers will not object to this definition. Tumor metabolism is the hottest and most dynamic direction in the field of cancer. In recent years, foreign researchers have realized that the metabolic level may also help us guide the precise classification of tumors. In the past two years, high-level studies in many top magazines have revealed the relationship between metabolic molecules and tumor typing and prognosis. For example, a study in Cell Metabolism reveals the metabolic heterogeneity of HGSOC through proteomics, metabolomics, etc., and also elucidates chronic oxidative stress and promyelocytic leukemia protein peroxisomes. The link between the proliferation-activated receptor co-activator 1α (PML-PGC-1α) axis (significant effect on the chemical sensitivity of the ovary). (Cell Metabolism: unveiling the "silent killer" veil, metabolomics + proteomics for high-grade serous ovarian cancer typing) and, in a study by Cancer Cell, 138 cases of renal clear cell carcinoma (ccRCC) The patient's cancer tissue was analyzed by metabolomics with normal tissues, and the ccRCC was molecularly classified at the metabolic level by joint analysis with transcriptome data and clinical information in the TGCA database. (Cancer Cell: How Metabolomics Plays with Large Queue Clinical Samples)
However, although the relationship between metabolism and tumors has been well studied, most studies focus on polar metabolites (such as amino acids, sugar metabolism, nucleotides, etc.), and the new cancer-promoting findings in this document The mechanism and target are lipid metabolism . In fact, lipids can be said to be involved in almost all physiological processes and diseases. Because lipids are an important part of biofilms, and biofilms constitute individual subcellular cells; at the same time, there are a large number of functional molecules on biofilms. For example, the study found that SOAT1 protein expression and cellular cholesterol It is closely related, and then participates in the proliferation and migration of tumor cells by affecting the abundance of the molecular integrin family. Therefore, changes in lipids can participate in most physiological and pathological processes by affecting the functions of macromolecules such as subcellular and receptors on the cell membrane. In addition, lipids are also important energy substances. The relationship between lipids and tumor development and treatment is still very rare. In other words, perhaps we can use the lipid group as a starting point to identify the key protein SOAT1 that regulates lipids by delineating abnormal changes in lipids.
to sum up:
This study not only allows us to see new hopes for the diagnosis and treatment of early liver cancer, but also sees the important value and application potential of proteomic technology applied to precision medicine. At the same time, we also see the importance of tumor metabolism (especially lipid metabolism). Sex and its research prospects. This research is bound to become an important milestone in the history of proteomics and precision medical development! Pay tribute to our researchers who are at the forefront of precision medicine! !
Protein|modification|metabolism|lipid|structural confirmation
T: 021-54665263
E:
Q: 1875681852
Fresh Half Shell Mussel Meat,Half Shell Mussel Meat,Frozen Cooked Mussel Meat,Frozen Mussel
Shengsi Xiangyuan Aquatic Products Co.,Ltd., , https://www.xiangyuan-aquatic.com