Scanning the brain with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) produces a number of 2-D "slices" that can be synthesized to build a 3-D presentation of the brain. Stroke patients often scan their brains in the hospital so that doctors can identify and identify damaged locations and areas. It usually takes 30 minutes to perform a high-resolution scan of the brain, but in the case of a stroke, this time is too long. Therefore, when a hospital receives a stroke patient, a rapid brain scan is performed. The interval between such fast scanning slices is 7 mm, while in high-end scientific research, slice scanning is usually performed at intervals of 1 mm. Doctors will analyze the effects of stroke on these scans, but often the resolution of such rapid clinical scans is too low, making many computer algorithms for assisted analysis difficult.
“These images are unique because they are obtained in clinical practice when patients are admitted to hospital due to a stroke,†said Polina Golland, professor of electrical engineering and computer science at MIT. “This kind of research is difficult for you to plan.â€
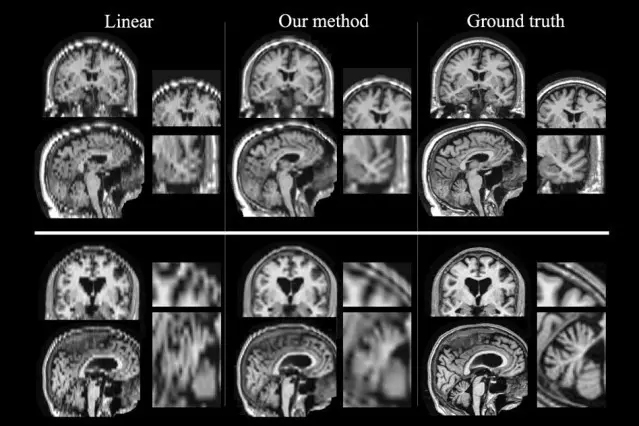
Artificial intelligence makes the original image with very low resolution clear (Source: MIT)
These hospital-based stroke scans are a wealth of data. To help scientists make better use of these scans, the research team from MIT, in collaboration with doctors and other institutions at the Massachusetts General Hospital, developed a way to improve the quality of these scans. Methods so that these clinical data can be used for large-scale stroke studies. Through these scans, researchers can investigate how genetic factors influence stroke survival and how patients respond to different treatment options. They can also use this route to study other diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease.
Fill in the data
For clinical scans of stroke patients, imaging is performed quickly due to the time limit of the scan, and the "slices" of the scan are very sparse, meaning that the sliced ​​images have a 5-7 mm gap. (On-chip resolution is 1mm)

Polina Golland, Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at MIT (Source: MIT)
Fire Protection Device,,Extinguisher,Home Fire Extinguisher
DONGGUAN TENYU TECH.INC , https://www.tenyutech.com