Drought stress is a global problem for plants. Will limit the growth and development of plants. Northwest is the largest producing area of ​​apple in China. Long-term moderate drought is an important factor limiting the development of apple industry. However, there are few studies on the molecular mechanism of fruit tree response to moderate drought stress.
Sample source
The leaf tissues of apple rootstocks were obtained from drought-sensitive materials M26 (drought treatment, control) and drought-tolerant material MBB (drought treatment, control).
Technical route
iTRAQ , three biological replicates
Research result
1. Physiological changes in response to moderate drought stress
The team determined the relative water content (RWC), leaf area (LA), specific leaf weight (LMA), free proline content (CFP), soluble sugar content (CSS), and malondialdehyde content (MDA) of the four groups. ). Physiological experiments showed that changes in RWC, CFP, CSS and MDA may affect the tolerance of apple rootstocks to moderate drought . Compared to M26, MBB is able to produce more osmotic adjustment substances under moderate drought stress.
2. Phosphorylation modification sites and identification of phosphorylated proteins
A total of 595 phosphorylated peptides, 682 phosphorylation sites and 446 phosphorylated proteins were identified. These 682 phosphorylation sites were located in serine (86.95%), threonine (11.73%), and tyrosine (1.32%), respectively.
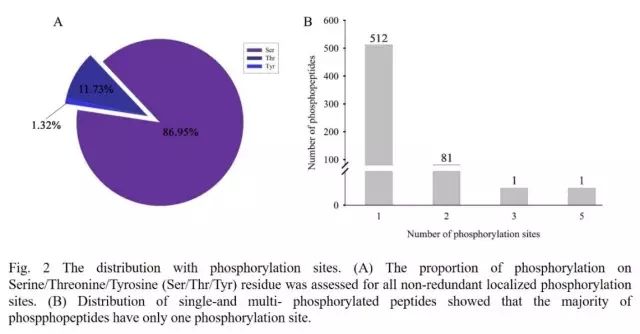
Phosphorylation modification site distribution
3. Differential phosphorylation protein identification and bioinformatics analysis
Compared with the control, the M26 and MBB under moderate drought stress showed significant changes in the phosphorylation levels of 5 and 35, respectively. Four of them are in both materials, which may be due to some similarities between the two genotypes in response to drought stress. Of the 446 proteins identified, 26 were protein kinases, 10 of which were common drought stress response kinases, but in this study, almost none of these kinases showed significant expression differences.
After obtaining differentially phosphorylated peptides and protein information, the team conducted a GO analysis . The results indicate that these differentially phosphorylated proteins are involved in metabolism, transcription, translation, and protein processing.
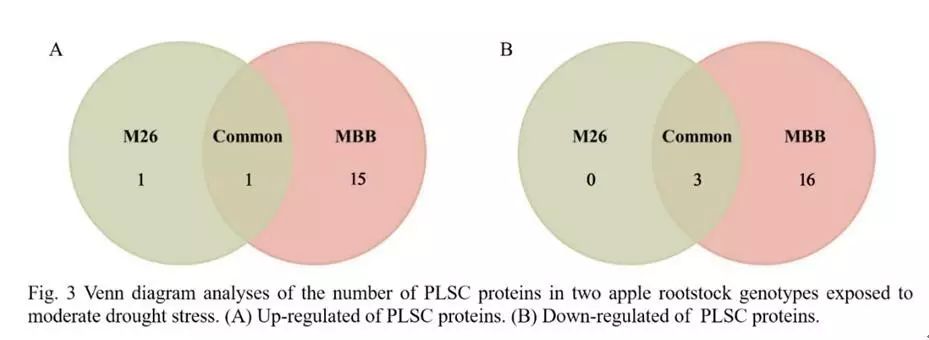
Venn diagram of differential proteins
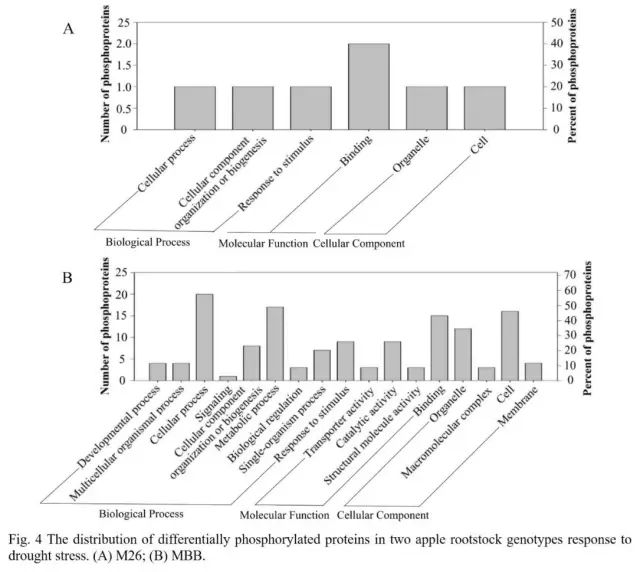
GO function analysis of differentially phosphorylated proteins
Subsequently, the team used motif-X to characterize the phosphorylation of differential proteins. The results showed that in the differentially phosphorylated proteins, the phosphorylation was located in serine, and [PxsP], [sP], [sD], [ Six modifications, such as Rxxs], [sxP] and [sxs], are the most common .
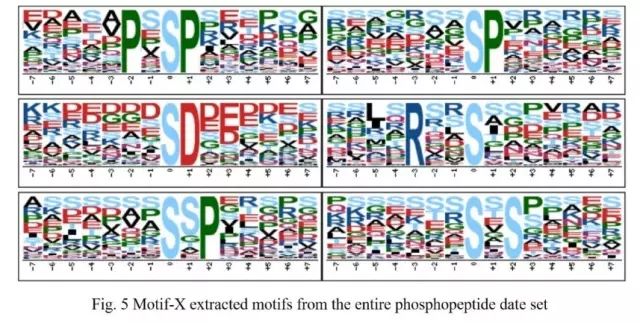
Analysis of modification characteristics of differentially phosphorylated proteins
4. qRT-PCR verification
The research team selected 17 genes for qRT-PCR validation. The results showed that the expression level of ACBP4 gene in M26 decreased, and the level of protein phosphorylation modification increased . In MBB, RPL5, eIF3B, Hsp70, Hsp70-90, DEK and TUBA3 increased significantly at the expression level, consistent with the trend of phosphorylation levels. These results indicate that under moderate drought stress, the mRNA of apple rootstock has a certain correlation with the change of protein phosphorylation.
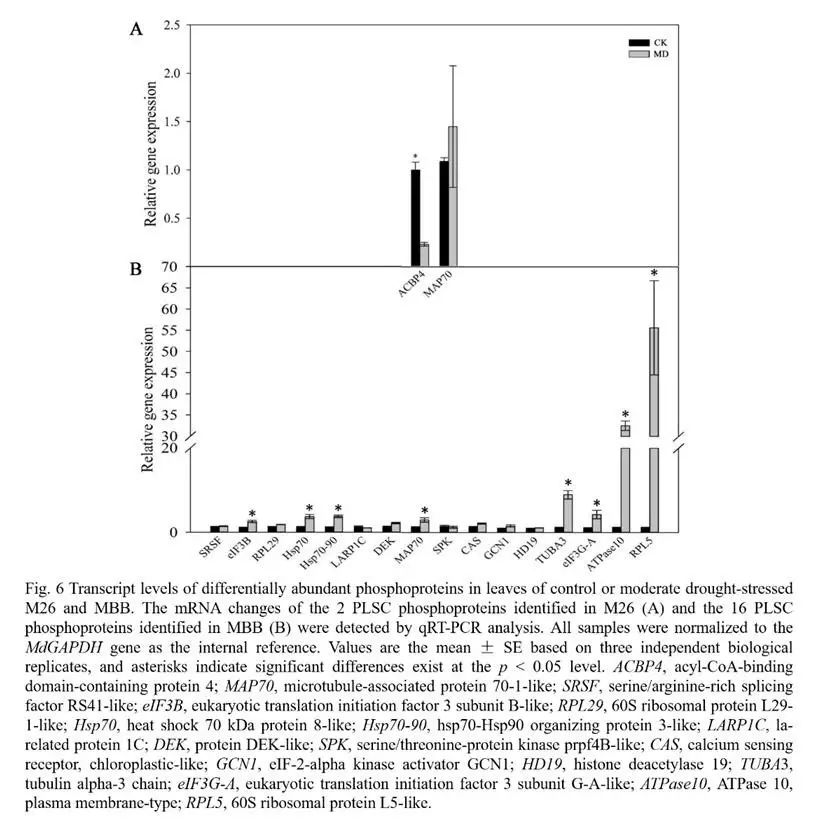
qRT-PCR verification
Xiaobian experience
In this paper, proteomics ( iTRAQ ) was used to compare the physiological and phosphorylated proteome of drought-sensitive genotype M26 and drought-tolerant MBB under moderate drought stress . Through the current common biometric analysis (GO, Motif-X) and verification means (qPCR), the target gene phosphorylation modified protein with higher credibility is obtained, which provides further molecular mechanism for moderate drought tolerance of Antao apple. A more accurate range of research.
X-Ray Protection Face Mask,Radiation Face Masks,Lead Acrylic Full Face Shield,Lead Masks In Radiology
Longkou Kangxie Medical Instrument Co., Ltd , https://www.sdkangxiemedical.com