Overview
Whey is a green, translucent liquid that is separated from the milk during the cheese production process and is a by-product of the production process. Whey Protein Isolate (WPI) is a dietary supplement extracted from it. Isolation of whey protein can be very pure, almost sugar-free and fat-free. The separation of whey protein is only about 0.7% in the whole milk, which is precious.
Isolated whey protein has high nutritional value and has become an important functional ingredient in various health foods. WPI is widely used in infant formula and is the best source of natural amino acids in infant growth and development. It is also widely used as an emulsifier and stabilizer in the food industry. WPI is also popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts because it can be quickly absorbed and digested to help improve the metabolic state of the body after exercise. It has been reported that WPI may have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties.
WPI consists of four main components: β- lactoglobulin (β-lactoglobulin), α- lactalbumin (α-lactalbumin), serum albumin (serum albumin), and immunoglobulins (Immunoglobulins).
Beta-lactoglobulin is a major component of WPI and is found in the milk of many other mammalian species. However, it does not exist in human breast milk. About 85% of children who are allergic to milk are no longer allergic after they are three years old, but 15% are still allergic. Beta-lactoglobulin is the major allergen in milk, so dairy producers need to label the presence or absence of beta-lactoglobulin to ensure that the needs of different consumers are met. Beta-lactoglobulin is a protein consisting of 162 amino acids with a molecular weight of 18.4 kDa and is present as a dimer under physiological conditions.
Alpha-lactalbumin is present in the milk of almost all mammalian species and is involved in the anabolism of lactose with a molecular weight of 14178 kDa.
Serum albumin is produced by the liver and functions mainly as a carrier protein in the blood, transporting steroids, fatty acids and thyroid hormones, which plays an important role in stabilizing extracellular fluid volume by contributing to colloid osmotic pressure. . Serum white eggs are water-soluble globular proteins with a molecular weight of approximately 65 kDa.
Immunoglobulins (Ig), also known as antibodies, are used by the immune system to recognize and neutralize foreign substances such as bacteria and viruses. There are five antibody isotypes in placental mammals, referred to as IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM, respectively. The immunoglobulin has a molecular weight of approximately 150 kDa.
Materials and Methods
Analytical testing using Malvern's Viscotek TDAmax multi-detector gel permeation chromatography system: Refractive Index Detector (RI), UV Detector (UV), 7° Angle Light Scattering (LALS), 90° Angular Light Scattering (RALS) ) and viscosity (IV) detectors.
â— The column is Viscotek p-columns series, 1 * P4000 and 1 * P3000.
The mobile phase was 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 7.0 with an injection volume of approximately 500 μg.
â— Data analysis processing using Omnisec software.
Results and discussion
1) Component analysis
The X axis is the retention volume, and the Y axis is the differential RI detector, the UV UV detector, the right angle light scattering RALS detector, the small angle light scattering LALS detector, and the viscosity DP detector.
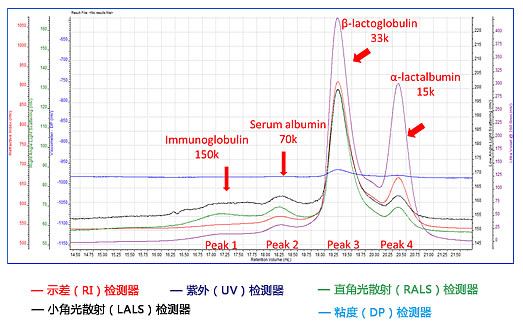
Immunoglobulin | Serum albumin | Beta-lactoglobulin | Alpha-lactal albumin | |
Peak retention volume - (ml) | 17.057 | 18.174 | 19.238 | 20.349 |
Number average molecular weight (Da) | 150,329 | 70,310 | 30,745 | 15,410 |
Weight average molecular weight (Da) | 151,366 | 70,469 | 31,847 | 15,549 |
Z average molecular weight (Da) | 152,485 | 70,635 | 33,125 | 15,697 |
Peak molecular weight (Da) | 127,955 | 69,619 | 30,683 | 15,800 |
Polydispersity Mw / Mn | 1.007 | 1.002 | 1.036 | 1.009 |
Intrinsic viscosity (dL/g) | 0.0596 | 0.0506 | 0.0339 | 0.0289 |
Hydrodynamic radius (nm) | 5.181 | 3.833 | 2.564 | 1.921 |
Component content (%) | 0.024 | 0.064 | 0.737 | 0.175 |
The dn/dc of all samples was set to 0.185.
The component of peak 3 shows a molecular weight of about 33 kDa, and the mass percentage in the component is about 75%. This component should be β-lactoglobulin, which is dimer in the active state and is in WPI. Main component.
The component of peak 4 is α-lactalbumin with a molecular weight of 15 kDa, which is in agreement with the theoretical value. An interesting finding is that α-lactalbumin showed a peak response less than half of β-lactoglobulin, and the UV-signal response of α-lactalbumin was very close to β-lactoglobulin, indicating that α-lactalbumin was at 280 nm. Beta-lactoglobulin has a higher UV extinction coefficient.
The molecular weights of peak 1 and peak 2 were 150 K and 70 K, respectively. According to the molecular weight, peak 1 was an immunoglobulin and peak 2 was serum albumin.
The polydispersity PD values ​​of all four peaks were less than 1.04, which is expected to match, in fact, all proteins are mono-distributed.
The separation mechanism of the gel chromatography is that the bulky component first flows out, the volume is small and then flows out, and the hydrodynamic radius Rh and the molecular weight result confirm that the lower molecular weight protein has a smaller size. The intrinsic viscosity also decreases with decreasing molecular weight, but is not linear, indicating differences between different protein structures. Β-lactoglobulin best explains this phenomenon. The molecular weight of β-lactoglobulin is about twice that of α-lactalbumin, and the intrinsic viscosity is only about 15% higher, which indicates the β-lactose of the dimer. The protein is more compact than the alpha-lactalbumin structure of the monomer.
2) Aggregate detection
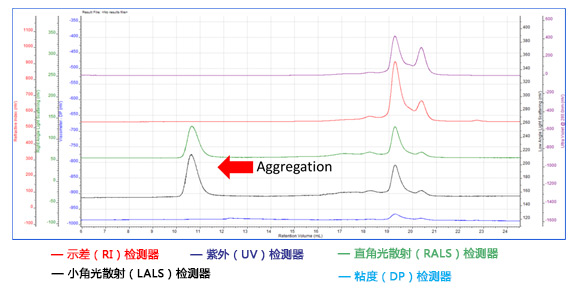
In the low retention volume of 10-12ml, both RALS and LALS peak, while RI or UV does not peak, RI and UV signals are proportional to the concentration, so the concentration of the component is very low; LS is proportional to the molecular weight and concentration multiplied by the molecular weight, so The molecular weight is only large to generate a light scattering peak. Another characteristic of the aggregated peak is that it has a low retention volume, indicating a large size. The viscosity detector also showed no peaks, indicating that the aggregates were very compact and therefore had low intrinsic viscosity.
in conclusion
The data reported in this application indicates that the Malvern Viscotek TDAmax multi-detector gel permeation chromatography system can be used to separate complex protein mixtures such as WPI. In this report, four components of WPI are obtained through a test: molecular weight, component content, hydrodynamic radius, and structure-related information of β-lactoglobulin, α-lactalbumin, serum albumin, and immunoglobulin. . Further, aggregates having a low concentration and being hardly detected by the RI difference were detected by light scattering. Such applications by Viscotek TDAmax make it an ideal method for food and nutrition application research, as well as protein research in the biopharmaceutical field.
(Author: Huang Lu, British Malvern Instruments GPC Application Specialist)
Seasoned Mixed Vegetables Slice
Seasoned Mixed Vegetables Slice,Seasoned Seaweed Mixed Vegetables,Seasoned Vegetables Slice,Mixed Vegetables Slice
DALIAN HAIBAO FOODS CO., LTD. , https://www.haibaoseafoods.com