First, yellow leaf seedlings
At first, the leaf color of the seedlings was light green and gradually turned yellow. When the seedlings were severe, the whole leaf withered and it was easy to cause empty stalks or baldness. Causes: The seeds are not full, the seedlings are not strong; the sowing is too deep, and the emergence is weak; the density is too high, which affects fertility; and the soil lacks fertilizer. Prevention and control measures: First, sow selected seeds before sowing, pick out grain, mold, bad grain, small grain, to ensure that the seeds of the degree of purity, purity are more than 98%, the germination rate of 90%. The second is germination sowing, seed coating or fertilizer soaking. The third is the appropriate time seedlings, in the corn 3-4 leaves when removed seedlings, weak seedlings, diseased seedlings and field weeds. The fourth is after the seedlings, make-up nitrogen fertilizer, and promote seedlings sooner. The fifth is that there are dry clumps before and after emergence, and dry clumps should be broken in time.
Second, albino seedlings
Generally from the 4 leaf stage, the leaf color at the base of the new leaf becomes light yellow-white, 5-6 leaf stage, and the lower 1-3 leaves of the heart appear pale yellow and light green stripes, but the veins are still green and the base appears Purple streak, after 10-15 days, the purple gradually becomes yellowish white, the leaf meat becomes thin, appearing as "white seedlings", and when it is severe, the whole field is white. Zinc-deficient corn plants are dwarf, with short internodes, overlapping leaf pillows, slow-growing hearts, and a flat top. In severe cases, white leaves gradually dry out, and the entire plant dies. The reason for this is the lack of zinc in the soil. Control measures: First, use zinc fertilizer as seed fertilizer, 1.5-2 kg of zinc sulfate per acre, and 15-20 kg of fine soil mixed evenly in the corn next to the seed sowing. The second is zinc fertilizer seed dressing, 1 kilogram of zinc sulfate and 25 kilograms of corn seeds. The method is to use 2-3 kilograms of warm water to dissolve 1 kilogram of zinc fertilizer. After the solution is completely dissolved, the zinc fertilizer solution is evenly sprayed onto the corn seeds to make the seeds. The surface is stained with zinc fertilizer and dried after sowing. The third is foliar spray of zinc fertilizer, for the emergence of zinc seedlings, with 0.2-0.3 kg of zinc sulfate per acre plus 100 kg of water for spraying, sprayed every 7 days, generally sprayed 2-3 times to make the seedlings Back to normal.
Third, purple red seedlings
The leaves and sheaths of seedlings changed from green to red and finally to purple. They generally appeared at the 3rd leaf stage of the maize and showed the most obvious at the 4-5 leaves. The roots were undeveloped, the stems were small and the growth was slow, and the leaves changed from green to purple. Leaves dead. The production of purple seedlings is mainly due to the lack of phosphorus in the soil, the loss of root absorption capacity, and the retardation of chlorophyll synthesis, resulting in the change of leaves from green to purple. After maize emerges, if it encounters a low temperature, it will often make the corn leaves become red or purple, but as the temperature rises, the phenomenon of red seedlings will gradually ease and disappear later. In addition, low-lying water in the field, harm to the underground pests, excessively viscous soil, too deep or too shallow sowing, and burning of seedlings caused by improper fertilization, improper treatment of pesticides, poisoning of seedlings, etc. can lead to red seedlings. Control measures: Increase the use of phosphate fertilizer as a base fertilizer, generally 40-50 kilograms of superphosphate and fermented organic fertilizer as base fertilizer. Once the purple seedlings appear, they can be sprayed with 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate for 2-3 times; level the land and dig the drains so that the rain stops and the fields do not accumulate water.
Fourth, yellow green seedlings
The seedlings of the corn seedlings are narrow and narrow, and the plants have short stature. The leaves appear yellow and green stripes, and when severe, the leaves are dark brown, and the coke is finally dead. Symptoms start from the lower leaves and gradually transfer to the upper leaves, affecting the yield, and prone to lodging. The reason for this is the lack of potassium in the soil. Prevention and control measures: Potassium fertilizer is added, and if no potassium fertilizer is used, plant ash can be used at the seedling stage, and potassium deficiency is severe. In the 3-leaf stage, potassium dihydrogen phosphate or ash leaching solution is sprayed on the leaf surface, the effect is immediate, and the yield increase is obvious.
Five, stiff leaf seedlings
Occurred mainly in the three-leaf stage of seedlings, the performance of small seedlings, light green leaves, increased black roots, soft cotton atrophy. After transplanting, with the exception of the new leaves appearing green, the outer leaves are yellow and stiff, with poor resistance, and they are prone to dead leaves and dead seedlings. Cause: The soil is too hard; the proportion of chemical fertilizer is too large, causing burned roots and buds to appear stiff seedlings; the soil is too dry after sowing. Prevention measures: Reasonable adjustment of fertilizer, water and gas conditions. During the seedling stage, organic fertilizers are mainly used for composting, and no or less urea is used as the base fertilizer. Phosphorus fertilizer should be applied after tanning. The soil is kept at a suitable humidity and the strong seedlings are transplanted. There have been stiff seedlings to strengthen the management of fertilizers and waters, promote their recovery as soon as possible, and promptly make up the seedlings in a timely manner.
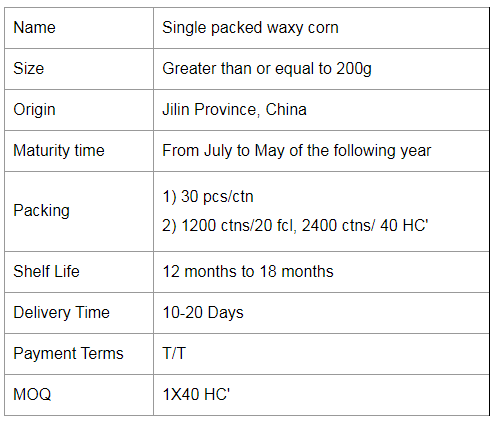
Single Packed Mottled Waxy Corn
Waxy corn comes in a variety of colours. Some people wonder if waxy corn is a genetically modified product. In fact, it is not. Waxy corn originated in China. It is caused by a genetic mutation. Artificial selection gradually led to the emergence of a type of tannin.
Waxy corn, also known as waxy corn, is sticky corn. The grain has coarse, waxy endosperm, similar to shiny, glassy (clear) grains such as hard and dented corn. Its chemical and physical characteristics are controlled by a recessive gene (wx), which is located on chromosome 9. 100% of the starch in the endosperm is straight-chain starch.
Coloured glutinous corn is generally white, yellow, red, purple and black, with white, yellow and purple corn being the basic colours. Purple and white hybrids naturally become purple if the purple gene "beats" the white gene and vice versa, so if the two tie we see white and purple corn. Purple can turn into red and black corn, or as we often say, "red is purple and black is purple". Of these colourful corn, the most common yellow waxy corn is the most nutritious as it is rich in carotenoids...
Currently, the only genetically modified foods sold on the Chinese market are soybean oil and papaya. Waxy maize is a hybrid variety and is not associated with genetic modification. Therefore, it can be concluded that glutinous maize is a hybrid variety and has nothing to do with genetic modification.
Genetic modification is a type of "genetic engineering" in modern science and technology, which makes use of modern molecular biology techniques. Hybridisation is the mating of individuals of different genotypes to produce offspring that are different from the original "pure" breed. In a sense, it belongs to the natural exchange of genes that can occur in nature.
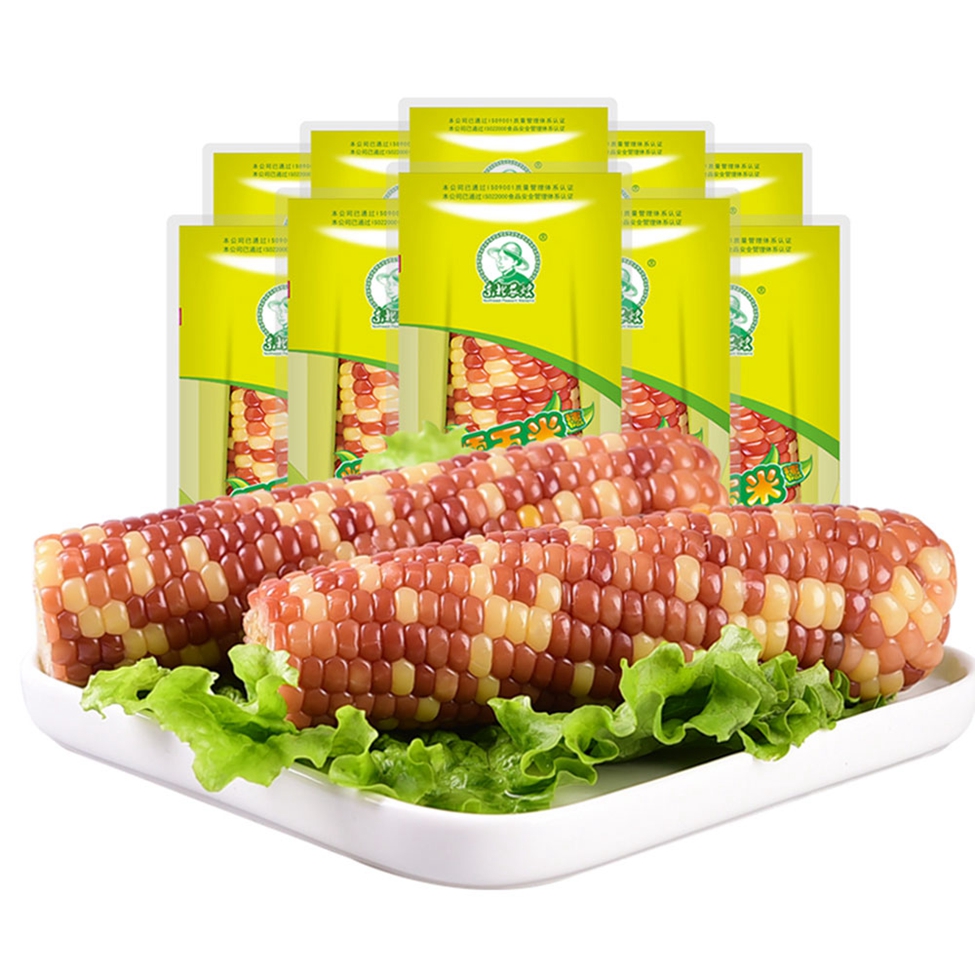
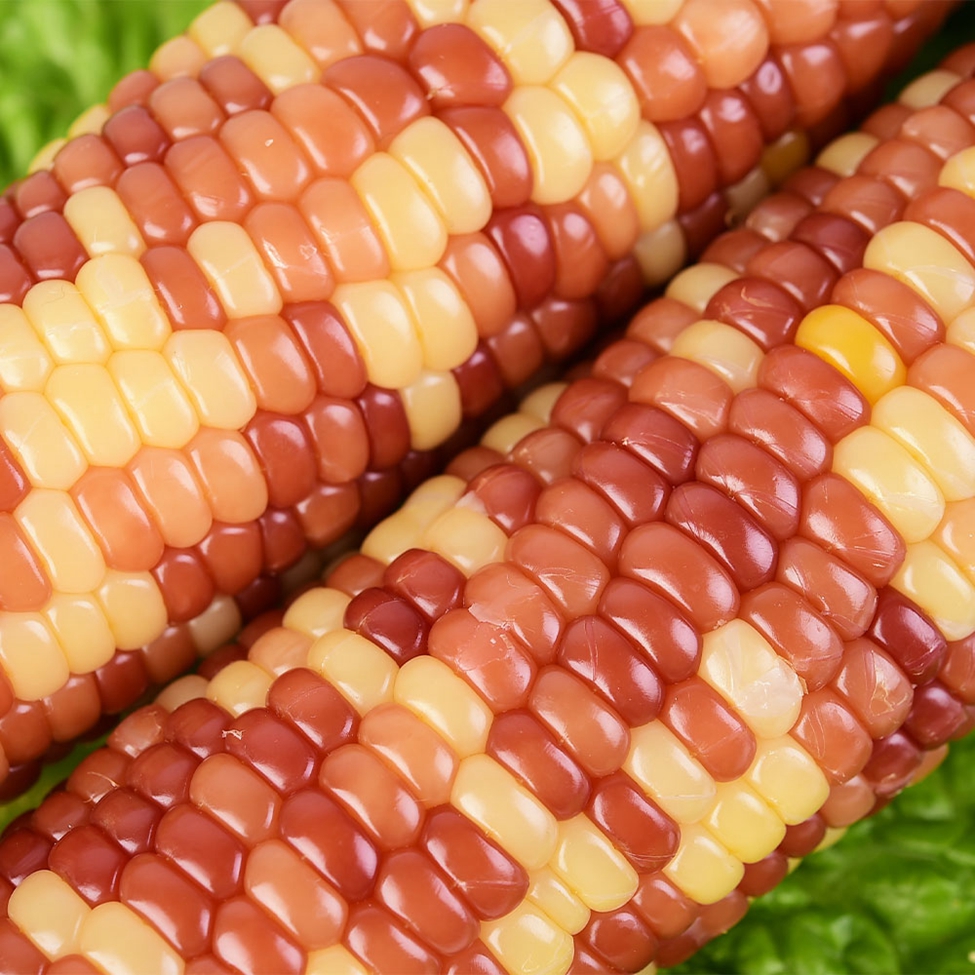


Colorful Waxy Corn,Colorful Mottled Waxy Corn,Single Packed Mottled Waxy Corn,Single Packed Colorful Waxy Corn
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorns.com